Does total hip arthroplasty restore native hip anatomy? three-dimensional reconstruction analysis
- PMID: 24966079
- PMCID: PMC4115107
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-014-2401-3
Does total hip arthroplasty restore native hip anatomy? three-dimensional reconstruction analysis
Abstract
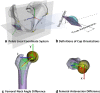
Purpose: Component orientations and positions in total hip arthroplasty (THA) are important parameters in restoring hip function. However, measurements using plain radiographs and 2D computed tomography (CT) slices are affected by patient position during imaging. This study used 3D CT to determine whether contemporary THA restores native hip geometry.
Methods: Fourteen patients with unilateral THA underwent CT scan for 3D hip reconstruction. Hip models of the nonoperated side were mirrored with the implanted side to quantify the differences in hip geometry between sides.
Results: The study demonstrated that combined hip anteversion (sum of acetabular and femoral anteversion) and vertical hip offset significantly increased by 25.3° ± 29.3° (range, -25.7° to 55.9°, p = 0.003) and 4.1 ± 4.7 mm (range, -7.1 to 9.8 mm, p = 0.009) in THAs.
Conclusions: These data suggest that hip anatomy is not fully restored following THA compared with the contralateral native hip.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Do post-operative changes of neck-shaft angle and femoral component anteversion have an effect on clinical outcome following uncemented total hip arthroplasty?Bone Joint J. 2015 Dec;97-B(12):1615-22. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.97B12.34654. Bone Joint J. 2015. PMID: 26637674
-
Does haptic robot-assisted total hip arthroplasty better restore native acetabular and femoral anatomy?Int J Med Robot. 2016 Jun;12(2):288-95. doi: 10.1002/rcs.1663. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Int J Med Robot. 2016. PMID: 25906764
-
Does acetabular retroversion affect range of motion after total hip arthroplasty?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011 Jan;469(1):218-24. doi: 10.1007/s11999-010-1482-6. Epub 2010 Jul 28. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011. PMID: 20665139 Free PMC article.
-
The Safe Zone Range for Cup Anteversion Is Narrower Than for Inclination in THA.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018 Feb;476(2):325-335. doi: 10.1007/s11999.0000000000000051. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018. PMID: 29529664 Free PMC article.
-
Two-Dimensional Versus Three-Dimensional Preoperative Planning in Total Hip Arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2024 Sep;39(9S1):S80-S87. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2024.05.054. Epub 2024 May 27. J Arthroplasty. 2024. PMID: 38810812 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
How to best measure femoral length and lateralisation after total hip arthroplasty on antero-posterior pelvic radiographs.Int Orthop. 2016 Dec;40(12):2479-2485. doi: 10.1007/s00264-016-3145-z. Epub 2016 Mar 1. Int Orthop. 2016. PMID: 26928723
-
Efficacy of an artificial intelligence preoperative planning system for assisting in revision surgery after artificial total hip arthroplasty.BMC Surg. 2025 Feb 7;25(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12893-024-02752-1. BMC Surg. 2025. PMID: 39920717 Free PMC article.
-
Biplanar Low-Dose Radiography Is Accurate for Measuring Combined Anteversion After Total Hip Arthroplasty.HSS J. 2020 Feb;16(1):23-29. doi: 10.1007/s11420-018-09659-7. Epub 2019 Feb 5. HSS J. 2020. PMID: 32015737 Free PMC article.
-
Robotic arm-assisted total hip arthroplasty for preoperative planning and intraoperative decision-making.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Aug 21;18(1):608. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-04095-8. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 37605281 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Loss of Knee Flexion and Femoral Rollback of the Medial-Pivot and Posterior-Stabilized Total Knee Arthroplasty During Early-Stance of Walking in Chinese Patients.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Jun 24;9:675093. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.675093. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34249882 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barrack RL. Dislocation after total hip arthroplasty: implant design and orientation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2003;11:89–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

