Design and Analysis for Studying microRNAs in Human Disease: A Primer on -Omic Technologies
- PMID: 24966218
- PMCID: PMC4082346
- DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwu135
Design and Analysis for Studying microRNAs in Human Disease: A Primer on -Omic Technologies
Abstract
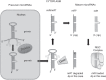
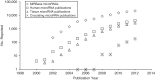
microRNAs (miRNAs) are fundamental to cellular biology. Although only approximately 22 bases long, miRNAs regulate complex processes in health and disease, including human cancer. Because miRNAs are highly stable in circulation when compared with several other classes of nucleic acids, they have generated intense interest as clinical biomarkers in diverse epidemiologic studies. As with other molecular biomarker fields, however, miRNA research has become beleaguered by pitfalls related to terminology and classification; procedural, assay, and study cohort heterogeneity; and methodological inconsistencies. Together, these issues have led to both false-positive and potentially false-negative miRNA associations. In this review, we summarize the biological rationale for studying miRNAs in human disease with a specific focus on circulating miRNAs, which highlight some of the most challenging topics in the field to date. Examples from lung cancer are used to illustrate the potential utility and some of the pitfalls in contemporary miRNA research. Although the field is in its infancy, several important lessons have been learned relating to cohort development, sample preparation, and statistical analysis that should be considered for future studies. The goal of this primer is to equip epidemiologists and clinical researchers with sound principles of study design and analysis when using miRNAs.
Keywords: blood; cancer; circulating biomarkers; lung cancer; microRNA; review.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell. 1993;75(5):855–862. - PubMed
-
- Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M, et al. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2000;403(6772):901–906. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Ambros V. An extensive class of small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 2001;294(5543):862–864. - PubMed
-
- Lim LP, Glasner ME, Yekta S, et al. Vertebrate microRNA genes. Science. 2003;299(5612):1540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

