Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced hepatitis by inhibiting apoptosis and autophagy pathways
- PMID: 24966472
- PMCID: PMC4055384
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/935251
Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced hepatitis by inhibiting apoptosis and autophagy pathways
Abstract
Background: Hepatic ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury is an important clinical problem, and its consequences can seriously threaten human health. Apoptosis and autophagy have been shown to contribute to cell death in hepatic I/R injury. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is the third most common endogenously produced gaseous signaling molecule and is known to exert a protective effect against hepatic I/R injury. In this study, the purpose is to explore both the effect and mechanism of H2S on hepatic I/R injury.
Methods: Balb/c mice were randomized into Sham, I/R, or two doses (14 μmol/kg and 28 μmol/kg) of sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS, an H2S donor) preconditioning groups.
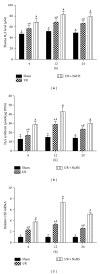
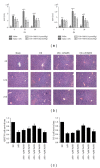
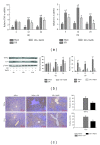
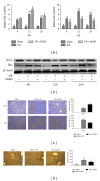
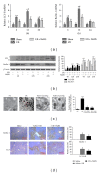
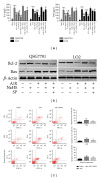
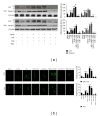
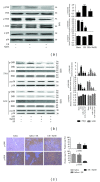
Results: NaHS significantly reduced the levels of TNF- α and IL-6 at 12 h and 24 h after injection compared with ischemia/reperfusion challenge alone. The expression of Bcl-2, Bax, Beclin-1, and LC3, which play important roles in the regulation of the apoptosis and autophagy pathways, was also clearly affected by NaHS. Furthermore, NaHS affected the p-JNK1, p-ERK1, and p-p38.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that H2S attenuates hepatic I/R injury, at least in part, by regulating apoptosis through inhibiting JNK1 signaling. The autophagy agonist rapamycin potentiated this hepatoprotective effect by reversing the inhibition of autophagy by H2S.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hydrogen sulfide preconditioning protects rat liver against ischemia/reperfusion injury by activating Akt-GSK-3β signaling and inhibiting mitochondrial permeability transition.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 13;8(9):e74422. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074422. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24058562 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen sulfide, a potential novel drug, attenuates concanavalin A-induced hepatitis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014 Sep 9;8:1277-86. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S66573. eCollection 2014. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014. PMID: 25246769 Free PMC article.
-
Ethyl pyruvate ameliorates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting intrinsic pathway of apoptosis and autophagy.Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:461536. doi: 10.1155/2013/461536. Epub 2013 Dec 25. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 24453420 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Hydrogen Sulfide in Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury.Biomolecules. 2024 Jun 22;14(7):740. doi: 10.3390/biom14070740. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effect of Hydrogen Sulfide on Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Jan;43(1):15-25. doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01166-4. Epub 2022 Jan 23. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 35066714 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
15-Deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2 alleviates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice via inducing antioxidant response and inhibiting apoptosis and autophagy.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017 May;38(5):672-687. doi: 10.1038/aps.2016.108. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017. PMID: 28216619 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of astaxanthin on ConA-induced autoimmune hepatitis by the JNK/p-JNK pathway-mediated inhibition of autophagy and apoptosis.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 11;10(3):e0120440. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120440. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25761053 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin prevents hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation and reducing autophagy via the TGF-β1/Smads and PI3K/Akt pathways.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 24;7(1):9289. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09673-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28839277 Free PMC article.
-
Astaxanthin Pretreatment Attenuates Hepatic Ischemia Reperfusion-Induced Apoptosis and Autophagy via the ROS/MAPK Pathway in Mice.Mar Drugs. 2015 May 27;13(6):3368-87. doi: 10.3390/md13063368. Mar Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26023842 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and Molecular Insights of Hydrogen Sulfide Signaling and Protein Sulfhydration.J Mol Biol. 2017 Feb 17;429(4):543-561. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.12.015. Epub 2016 Dec 21. J Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28013031 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dogan S, Aslan M. Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury and therapeutic strategies to alleviate cellular damage. Hepatology Research. 2011;41(2):103–117. - PubMed
-
- Shi J, Li XH, Sun BC, et al. Protective functions of recombinant protein targeted at RANKL against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury transfected by retrovirus in mice. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011;91(38):2719–2724. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

