Alkaline phosphatase: an overview
- PMID: 24966474
- PMCID: PMC4062654
- DOI: 10.1007/s12291-013-0408-y
Alkaline phosphatase: an overview
Abstract
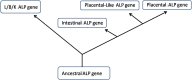
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP; E.C.3.I.3.1.) is an ubiquitous membrane-bound glycoprotein that catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphate monoesters at basic pH values. Alkaline phosphatase is divided into four isozymes depending upon the site of tissue expression that are Intestinal ALP, Placental ALP, Germ cell ALP and tissue nonspecific alkaline phosphatase or liver/bone/kidney (L/B/K) ALP. The intestinal and placental ALP loci are located near the end of long arm of chromosome 2 and L/B/K ALP is located near the end of the short arm of chromosome 1. Although ALPs are present in many mammalian tissues and have been studied for the last several years still little is known about them. The bone isoenzyme may be involved in mammalian bone calcification and the intestinal isoenzyme is thought to play a role in the transport of phosphate into epithelial cells of the intestine. In this review, we tried to provide an overview about the various forms, structure and functions of alkaline phosphatase with special focus on liver/bone/kidney alkaline phosphatase.
Keywords: Alkaline phosphatase; Enzymes; Intestinal alkaline phosphatase; Isoenzymes; L/B/K alkaline phosphatase; Liver alkaline phosphatase; Placental alkaline phosphatase.
Figures




References
-
- McComb RB, Bowers GN, Posen S. Alkaline phosphatase. New York: Plenum Publishing Corp; 1979.
-
- Whyte MP, Landt M, Ryan LM, Mulivor RA, Henthorn PS, Fedde KN, Mahuren JD, Coburn SP. Alkaline phosphatase: placental and tissue-nonspecific isoenzymes hydrolyze phosphoethanolamine, inorganic pyrophosphate, and pyridoxal 5′-phosphate substrate accumulation in carriers of hypophosphatasia corrects during pregnancy. J Clin Invest. 1995;95:1440–1445. doi: 10.1172/JCI117814. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
