In-vitro Behavior of Human Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells Towards Serum Based Minimal Cytokine Growth Conditions
- PMID: 24966475
- PMCID: PMC4062666
- DOI: 10.1007/s12291-013-0346-8
In-vitro Behavior of Human Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells Towards Serum Based Minimal Cytokine Growth Conditions
Abstract
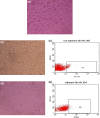
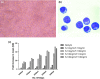
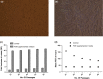
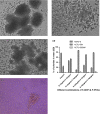
We tried here to optimize the proliferation of both Hematopoietic and Mesenchymal stem cells of Umbilical Cord blood in minimal cytokine growth condition. Failing to get good results of expansion of non-adherent Hematopoietic Total Nucleated Cells and adherent Fibroblastic Mesenchymal Stem Cells derived from 10-12 ml of collected Cord blood, we designed the further experimental study by increasing the volume of Cord blood sample up to 65-70 ml. We harvested the non-adherent as well as adherent fraction separately derived from the primary culture of Umbilical Cord blood stem cells under the influence of growth promoting Cytokines or Growth Factors. The proliferation study was conducted by taking different combinations of two hematopoietic growth stimulatory Cytokines like stem cell factor (SCF) and Fms like tyrosine kinase-3Ligand (Flt3L) at concentrations (10 ng/ml, 100 ng/ml) while we preferred Mesenchymal specific growth factor i.e. basic Fibroblast growth factor (FGF-β) at its 10 ng/ml concentration for adherent cells to get optimal results. The Hematopoietic and Fibroblast Colony forming abilities of the expanded stem cells were performed through Colony Forming Unit assay. Culture Medium containing cytokine combination like SCF 100 ng/ml with Flt3L 10 ng/ml was found to be optimal for the proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells. But the number of hematopoietic colonies like Erythroid colonies generated were less in case of media supplemented with SCF & Flt3L while more number of Myeloid colonies were observed in Growth factor supplemented media in comparison to the control one. The FGF-β supplemented media successfully enhanced the proliferation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and exhibited its efficient Fibroblast colony forming ability. Our experimental study supports the minimal utilization of cytokines for haematopoietic and mesenchymal stem cell proliferation which may help in future safe Cord blood stem cell infusion.
Keywords: Adherent cells; Cytokines; Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs); Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs); Non-adherent cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cell-based or umbilical vein endothelial cell-based serum-free coculture with cytokines supports the ex vivo expansion/maintenance of cord blood hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Dec 5;10(1):376. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1502-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31806004 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous expansion and harvest of hematopoietic stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord blood.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010 Dec;21(12):3183-93. doi: 10.1007/s10856-010-4167-5. Epub 2010 Oct 6. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010. PMID: 20924776
-
Mesenchymal stem cells feeder layer from human umbilical cord blood for ex vivo expanded growth and proliferation of hematopoietic progenitor cells.Ann Hematol. 2006 Apr;85(4):212-25. doi: 10.1007/s00277-005-0047-3. Epub 2006 Jan 4. Ann Hematol. 2006. PMID: 16391912
-
Differential ability of MSCs isolated from placenta and cord as feeders for supporting ex vivo expansion of umbilical cord blood derived CD34(+) cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015 Oct 19;6:201. doi: 10.1186/s13287-015-0194-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26481144 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of FLT3 receptor and response to FLT3 ligand by leukemic cells.Leukemia. 1996 Apr;10(4):588-99. Leukemia. 1996. PMID: 8618433 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of CD34+ and CD90+ Stem Cells of Cord Blood with Neonatal Factors: A Cross-sectional Study.Indian J Pediatr. 2016 Feb;83(2):114-9. doi: 10.1007/s12098-015-1839-7. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Indian J Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 26245655
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
