Estimation of Ischemia Modified Albumin (IMA) Levels in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome
- PMID: 24966488
- PMCID: PMC4062667
- DOI: 10.1007/s12291-013-0367-3
Estimation of Ischemia Modified Albumin (IMA) Levels in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome
Abstract
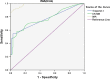
Myocardial ischemia produces free radicals that catalyze a series of oxidative reactions that damage healthy tissues. The N-terminal sequence of albumin is one of the proteins modified by these highly reactive oxygen species and forms the ischemia modified albumin (IMA). This study involves investigations undertaken in different study groups to assess the levels of IMA. Mean serum IMA levels (U/mL) in patients with ST-segment elevated myocardial infarction (92.1 ± 10.6), non-ST-segment elevated myocardial infarction (87.3 ± 5.95) and unstable angina (UA) (88.9 ± 6.16) were significantly higher than non-cardiac chest pain (77.9 ± 6.69) and also healthy subjects (54.7 ± 17.2) (p < 0.001). IMA is a highly sensitive marker and has a high predictive value, which might prove the usefulness of this biomarker for early detection of myocardial ischemia. These data indicate a possible role of the IMA test in the early triage of patients with chest pain.
Keywords: Acute coronary syndrome; Biomarker; Ischemia; Ischemia modified albumin; Reactive oxygen species.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ischemia-modified albumin: is it a promising marker in acute coronary syndrome?BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Aug 22;24(1):436. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04108-2. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39174920 Free PMC article.
-
Ischemia-modified albumin in differential diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome without ST elevation and unstable angina pectoris.Kardiol Pol. 2010 Apr;68(4):431-7. Kardiol Pol. 2010. PMID: 20425705
-
A Comparative Study of Ischemia-Modified Albumin: A Promising Biomarker for Early Detection of Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS).Cureus. 2023 Aug 30;15(8):e44357. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44357. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37779796 Free PMC article.
-
[Ischemia modified albumin--specific marker in cardiological diagnostics?].Wiad Lek. 2008;61(10-12):263-8. Wiad Lek. 2008. PMID: 19323066 Review. Polish.
-
Ischemia-Modified Albumin as a Marker of Acute Coronary Syndrome: The Case for Revising the Concept of "N-Terminal Modification" to "Fatty Acid Occupation" of Albumin.Dis Markers. 2017;2017:5692583. doi: 10.1155/2017/5692583. Epub 2017 Mar 5. Dis Markers. 2017. PMID: 28356609 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Histidine-Bound Dinitrosyl Iron Complexes: Antioxidant and Antiradical Properties.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 7;24(24):17236. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417236. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139065 Free PMC article.
-
A synergistic role of ischemia modified albumin and high-sensitivity troponin T in the early diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome.J Family Med Prim Care. 2015 Oct-Dec;4(4):570-5. doi: 10.4103/2249-4863.174295. J Family Med Prim Care. 2015. PMID: 26985418 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers in acute myocardial infarction: current perspectives.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2019 Jan 17;15:1-10. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S166157. eCollection 2019. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2019. PMID: 30697054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Ischemia-Modified Albumin for Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Apr 28;58(5):614. doi: 10.3390/medicina58050614. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35630031 Free PMC article.
-
Ischemia modified albumin (IMA) in acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and left bundle branch block (LBBB). Does it make the difference?Egypt Heart J. 2017 Sep;69(3):183-190. doi: 10.1016/j.ehj.2017.01.004. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Egypt Heart J. 2017. PMID: 29622975 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources