A comparative study of oxytocin/misoprostol/methylergometrine for active management of the third stage of labor
- PMID: 24966500
- PMCID: PMC4061329
- DOI: 10.1007/s13224-014-0512-9
A comparative study of oxytocin/misoprostol/methylergometrine for active management of the third stage of labor
Abstract
Objectives: To study oxytocin, misoprostol, and methylergometrine in active management of the third stage of labor and determine duration of the third stage of labor, blood loss, adverse effects, and need for additional uterotonics in each group.
Methods: Clinical trial of 300 women with healthy singleton pregnancy allocated into three groups to receive either: 10 IU intravenous oxytocin infusion, 600 μg sublingual misoprostol, or 200 μg intravenous methylergometrine. Primary outcome measure was blood loss in the third stage of labor; secondary measures were duration of the third stage, side effects, and complications.
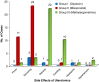
Results: Subjects who received 600 μg of misoprostol had the least blood loss, followed by oxytocin, and methylergometrine. The shortest mean duration of the third stage was with misoprostol. Shivering and pyrexia were observed in misoprostol group, and raised blood pressure in methylergometrine group.
Conclusions: Misoprostol is as effective as oxytocin and both are more effective than methylergometrine in active management of the third stage of labor.
Keywords: Active management; PPH; Third stage.
References
-
- Mathai M, Gülmezoglu A, Hill S. WHO recommendations for the prevention of postpartum hemorrhage. Geneva: WHO Document Production Services; 2007. pp. 4–5.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources