Three-dimensional imaging techniques: A literature review
- PMID: 24966761
- PMCID: PMC4054026
- DOI: 10.4103/1305-7456.126269
Three-dimensional imaging techniques: A literature review
Abstract
Imaging is one of the most important tools for orthodontists to evaluate and record size and form of craniofacial structures. Orthodontists routinely use 2-dimensional (2D) static imaging techniques, but deepness of structures cannot be obtained and localized with 2D imaging. Three-dimensional (3D) imaging has been developed in the early of 1990's and has gained a precious place in dentistry, especially in orthodontics. The aims of this literature review are to summarize the current state of the 3D imaging techniques and to evaluate the applications in orthodontics.
Keywords: 3D imaging; 3D scanning; orthodontic diagnosis; treatment planning.
Conflict of interest statement
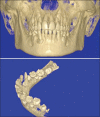
Figures


References
-
- Webber RL, Horton RA, Tyndall DA, Ludlow JB. Tuned-aperture computed tomography (TACT). Theory and application for three-dimensional dento-alveolar imaging. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 1997;26:53–62. - PubMed
-
- Ucar FI, Sekerci AE, Uysal T, Bengi AO. Standardization of records in orthodontics. Part 2: Craniofacial imaging techniques. Turkish Journal of Orthodontics. 2012;25:167–87.
-
- Hajeer MY, Millett DT, Ayoub AF, Siebert JP. Applications of 3D imaging in orthodontics: Part 1. J Orthod. 2004;31:62–70. - PubMed
-
- Plooij JM, Maal TJ, Haers P, Borstlap WA, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM, Bergé SJ. Digital three-dimensional image fusion processes for planning and evaluating orthodontics and orthognathic surgery. A systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;40:341–52. - PubMed
-
- Mavili ME, Canter HI, Saglam-Aydinatay B, Kamaci S, Kocadereli I. Use of three-dimensional medical modeling methods for precise planning of orthognathic surgery. J Craniofac Surg. 2007;18:740–7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

