Dual expression of Epstein-Barr virus, latent membrane protein-1 and human papillomavirus-16 E6 transform primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts through NF-κB signaling
- PMID: 24966902
- PMCID: PMC4069875
Dual expression of Epstein-Barr virus, latent membrane protein-1 and human papillomavirus-16 E6 transform primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts through NF-κB signaling
Abstract
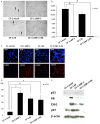
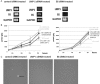
The prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and high-risk human papilloma virus (HPV) infections in patients with oral cancer in Okinawa, southwest islands of Japan, has led to the hypothesis that carcinogenesis is related to EBV and HPV co-infection. To explore the mechanisms of transformation induced by EBV and HPV co-infection, we analyzed the transformation of primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) expressing EBV and HPV-16 genes, alone or in combination. Expression of EBV latent membrane protein-1 (LMP-1) alone or in combination with HPV-16 E6 increased cell proliferation and decreased apoptosis, whereas single expression of EBV nuclear antigen-1 (EBNA-1), or HPV-16 E6 did not. Co-expression of LMP-1 and E6 induced anchorage-independent growth and tumor formation in nude mice, whereas expression of LMP-1 alone did not. Although the singular expression of these viral genes showed increased DNA damage and DNA damage response (DDR), co-expression of LMP-1 and E6 did not induce DDR, which is frequently seen in cancer cells. Furthermore, co-expression of LMP-1 with E6 increased NF-κB signaling, and the knockdown of LMP-1 or E6 in co-expressing cells decreased cell proliferation, anchorage independent growth, and NF-κB activation. These data suggested that expression of individual viral genes is insufficient for inducing transformation and that co-expression of LMP-1 and E6, which is associated with suppression of DDR and increased NF-κB activity, lead to transformation. Our findings demonstrate the synergistic effect by the interaction of oncogenes from different viruses on the transformation of primary MEFs.
Keywords: E6; LMP-1; NF-κB; co-expression; primary mouse embryonic fibroblast; transformation.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
