Adenosine A2B receptor modulates intestinal barrier function under hypoxic and ischemia/reperfusion conditions
- PMID: 24966910
- PMCID: PMC4069946
Adenosine A2B receptor modulates intestinal barrier function under hypoxic and ischemia/reperfusion conditions
Abstract
Background: Intestinal barrier function failure from ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) and acute hypoxia has been implicated as a critical determinant in the predisposition to intestinal inflammation and a number of inflammatory disorders. Here, we identified the role of Adenosine A2B receptor (A2BAR) in the regulation of intestinal barrier function under I/R and acute hypoxic conditions.
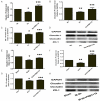
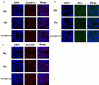
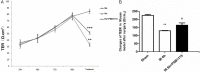
Methods: C57BL/6J mice were used, and were randomized into three groups: Sham, I/R, IR+PSB1115 (a specific A2BAR antagonist) groups. After surgery, the small bowel was harvested for immunohistochemical staining, RNA and protein content, and intestinal permeability analyses. Using an epithelial cell culture model, we investigated the influence of hypoxia on the epithelial function, and the role of A2BAR in the expressions of tight junction and epithelial permeability. The expressions of Claudin-1, occludin and ZO-1 were detected by RT-PCR and Western-Blot. Epithelial barrier function was assessed with transepithelial resistance (TER).
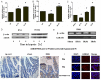
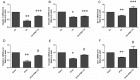
Results and conclusions: The A2BAR antagonist, PSB1115, significantly increased tight junction protein expression after intestinal I/R or acute hypoxia conditions. PSB1115 also attenuated the disrupted distribution of TJ proteins. Furthermore, inhibition of A2BAR attenuated the decrease in TER induced by I/R or acute hypoxic conditions, and maintained intestinal barrier function. Antagonism of A2BAR activity improves intestinal epithelial structure and barrier function in a mouse model of intestinal I/R and a cell model of acute hypoxia. These findings support a potentially destructive role for A2BAR under intestinal I/R and acute hypoxic conditions.
Keywords: Ischemia/reperfusion; TER; ZO-1; adenosine A2B receptor; claudin-1; hypoxia; occludin; tight junction.
Figures
References
-
- Daniel C, Sartory NA, Zahn N, Radeke HH, Stein JM. Immune modulatory treatment of trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid colitis with calcitriol is associated with a change of a T helper (Th) 1/Th17 to a Th2 and regulatory T cell profile. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;324:23–33. - PubMed
-
- Berland T, Oldenburg WA. Acute mesenteric ischemia. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2008;10:341–346. - PubMed
-
- Ogra PL, Welliver RC Sr. Effects of early environment on mucosal immunologic homeostasis, subsequent immune responses and disease outcome. Nestle Nutr Workshop Ser Pediatr Program. 2008;61:145–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
