A pilot project of early integrated traumatic brain injury rehabilitation in singapore
- PMID: 24967105
- PMCID: PMC4055383
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/950183
A pilot project of early integrated traumatic brain injury rehabilitation in singapore
Abstract
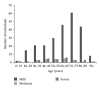
Objective. Document acute neurosurgical and rehabilitation parameters of patients of all traumatic brain injury (TBI) severities and determine whether early screening along with very early integrated TBI rehabilitation changes functional outcomes. Methods. Prospective study involving all patients with TBI admitted to a neurosurgical department of a tertiary hospital. They were assessed within 72 hours of admission by the rehabilitation team and received twice weekly rehabilitation reviews. Patients with further rehabilitation needs were then transferred to the attached acute inpatient TBI rehabilitation unit (TREATS) and their functional outcomes were compared against a historical group of patients. Demographic variables, acute neurosurgical characteristics, medical complications, and rehabilitation outcomes were recorded. Results. There were 298 patients screened with an average age of 61.8 ± 19.1 years. The most common etiology was falls (77.5%). Most patients were discharged home directly (67.4%) and 22.8% of patients were in TREATS. The TREATS group functionally improved (P < 0.001). Regression analysis showed by the intervention of TREATS, that there was a statistically significant FIM functional gain of 18.445 points (95% CI -30.388 to -0.6502, P = 0.03). Conclusion. Our study demonstrated important epidemiological data on an unselected cohort of patients with TBI in Singapore and functional improvement in patients who further received inpatient rehabilitation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Results from a prospective acute inpatient rehabilitation database: clinical characteristics and functional outcomes using the Functional Independence Measure.Ann Acad Med Singap. 2007 Jan;36(1):3-10. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2007. PMID: 17285180
-
The effect of age on functional outcome in mild traumatic brain injury: 6-month report of a prospective multicenter trial.J Trauma. 2004 May;56(5):1042-8. doi: 10.1097/01.ta.0000127767.83267.33. J Trauma. 2004. PMID: 15179244
-
Presence of a dedicated trauma center physiatrist improves functional outcomes following traumatic brain injury.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2016 Jan;80(1):70-5. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000000890. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2016. PMID: 26491804
-
Volumetric analysis of day of injury computed tomography is associated with rehabilitation outcomes after traumatic brain injury.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017 Jan;82(1):80-92. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000001263. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017. PMID: 27805992 Free PMC article.
-
Functional level during the first 2 years after moderate and severe traumatic brain injury.Brain Inj. 2015;29(12):1431-8. doi: 10.3109/02699052.2015.1063692. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Brain Inj. 2015. PMID: 26361939
Cited by
-
Functional Outcomes in Moderate-to-Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Survivors.J Emerg Trauma Shock. 2018 Jul-Sep;11(3):197-204. doi: 10.4103/JETS.JETS_6_18. J Emerg Trauma Shock. 2018. PMID: 30429628 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Early Interdisciplinary Rehabilitation for Trauma Patients: A Systematic Review.Arch Rehabil Res Clin Transl. 2020 Jun 25;2(4):100070. doi: 10.1016/j.arrct.2020.100070. eCollection 2020 Dec. Arch Rehabil Res Clin Transl. 2020. PMID: 33543097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changing Demographic Profiles of Patients With Traumatic Brain Injury: An Aging Concern.Front Surg. 2019 Jul 3;6:37. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2019.00037. eCollection 2019. Front Surg. 2019. PMID: 31334245 Free PMC article.
-
Adherence to Guidelines for Acute Rehabilitation in the Norwegian Trauma Plan.J Rehabil Med. 2023 Jun 27;55:jrm6552. doi: 10.2340/jrm.v55.6552. J Rehabil Med. 2023. PMID: 37366570 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baguley I, Slewa-Younan S, Lazarus R, Green A. Long-term mortality trends in patients with traumatic brain injury. Brain Injury. 2000;14(6):505–512. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Injury Prevention and Control: Traumatic Brain Injury, 2011, http://www.cdc.gov/TraumaticBrainInjury.
-
- Speech by Director of Medical Services, Prof K. Satkunanantham, at the Opening Ceremony of the 7th Singapore Trauma Conference, 2013, http://www.moh.gov.sg/content/moh_web/home/pressRoom/speeches_d/2013/spe....
-
- Lee KK, Seow WT, Ng I. Demographical profiles of adult severe traumatic brain injury patients: implications for healthcare planning. Singapore Medical Journal. 2006;47(1):31–36. - PubMed
-
- Finkelstein E, Corso P, Miller TR. The Incidence and Economic Burden of Injuries in the United States. New York, NY, USA: Oxford University Press; 2006.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources