Management of complicated and uncomplicated acute type B dissection. A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 24967162
- PMCID: PMC4052408
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2225-319X.2014.05.08
Management of complicated and uncomplicated acute type B dissection. A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The management of acute type B dissection represents a clinical challenge. We undertook a systematic review of the available literature regarding medical, surgical and endovascular treatments of acute type B aortic dissection and combined the eligible studies into a meta-analysis.
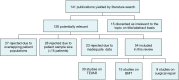
Methods: An extensive electronic health database search was performed on all articles published from January 2006 up to November 2013 describing the management of acute type B aortic dissection. Studies including less than 15 patients were excluded.
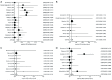
Results: ACUTE COMPLICATED TYPE B DISSECTION: overall, 2,531 patients were treated with endovascular repair (TEVAR) and the pooled rate for 30-day/in-hospital mortality was 7.3%. The pooled estimates for cerebrovascular events, spinal cord ischemia (SCI) and total neurologic events were 3.9%, 3.1% and 7.3%, respectively. A total of 1,276 patients underwent open surgical repair and the pooled rate for 30-day/in-hospital mortality was 19.0%. The pooled rate for cerebrovascular events was 6.8%, for SCI 3.3% and for total neurologic complications 9.8%. Acute uncomplicated type B dissection: outcome of 2,347 patients who underwent conservative medical management were analyzed. The pooled 30-day/in-hospital mortality rate was 2.4%. The pooled rate for cerebrovascular events was 1%, for SCI 0.8% and for overall neurologic complications 2%.
Conclusions: Endovascular repair provides a superior 30-day/in-hospital survival for acute complicated type B aortic dissection compared to surgical aortic reconstruction. However, open repair still has a significant role as endovascular repair is not applicable in all patients and there remains concerns regarding the durability of this technique. TEVAR seems to have a more favorable outcome regarding aortic remodeling and the aortic-specific survival rate when compared with medical therapy alone. Randomized controlled trials focusing on the prognostic factors of early and late complications in uncomplicated type B dissections are needed.
Keywords: Type B aortic dissection; acute; endovascular; medical treatment.
Figures


References
-
- Coady MA, Ikonomidis JS, Cheung AT, et al. Surgical management of descending thoracic aortic disease: open and endovascular approaches: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010;121:2780-804 - PubMed
-
- Fattori R, Cao P, De Rango P, et al. Interdisciplinary expert consensus document on management of type B aortic dissection. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013;61:1661-78 - PubMed
-
- Tsai TT, Trimarchi S, Nienaber CA. Acute aortic dissection: perspectives from the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD). Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2009;37:149-59 - PubMed
-
- Tsai TT, Evangelista A, Nienaber CA, et al. Long-term survival in patients presenting with type A acute aortic dissection: insights from the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD). Circulation 2006;114:I350-6 - PubMed
-
- Nienaber CA, Kische S, Rousseau H, et al. Endovascular repair of type B aortic dissection: long-term results of the randomized investigation of stent grafts in aortic dissection trial. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 2013;6:407-16 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
