Enhanced oral bioavailability of efavirenz by solid lipid nanoparticles: in vitro drug release and pharmacokinetics studies
- PMID: 24967360
- PMCID: PMC4055422
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/363404
Enhanced oral bioavailability of efavirenz by solid lipid nanoparticles: in vitro drug release and pharmacokinetics studies
Abstract
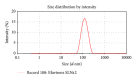
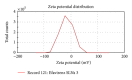
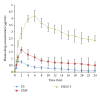
Solid lipid nanoparticle is an efficient lipid based drug delivery system which can enhance the bioavailability of poorly water soluble drugs. Efavirenz is a highly lipophilic drug from nonnucleoside inhibitor category for treatment of HIV. Present work illustrates development of an SLN formulation for Efavirenz with increased bioavailability. At first, suitable lipid component and surfactant were chosen. SLNs were prepared and analyzed for physical parameters, stability, and pharmacokinetic profile. Efavirenz loaded SLNs were formulated using Glyceryl monostearate as main lipid and Tween 80 as surfactant. ESLN-3 has shown mean particle size of 124.5 ± 3.2 nm with a PDI value of 0.234, negative zeta potential, and 86% drug entrapment. In vitro drug release study has shown 60.6-98.22% drug release in 24 h by various SLN formulations. Optimized SLNs have shown good stability at 40°C ± 2°C and 75 ± 5% relative humidity (RH) for 180 days. ESLN-3 exhibited 5.32-fold increase in peak plasma concentration (C max) and 10.98-fold increase in AUC in comparison to Efavirenz suspension (ES).
Figures
References
-
- Sahoo SK, Labhasetwar V, editors. Nanoparticles Interface: An Important Determinant in nanoparticle-Mediated Drug/Gene Delivery. Nanoparticle Technology for Drug Delivery. New York, NY, USA: Taylor & Francis; 2006.
-
- Vyas SP, Khar RK, editors. Nanoparticles. Targeted and Controlled Drug Delivery—Novel Carrier Systems. New Delhi, India: CBS; 2002.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources