Character displacement of Cercopithecini primate visual signals
- PMID: 24967517
- PMCID: PMC4110701
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms5266
Character displacement of Cercopithecini primate visual signals
Abstract
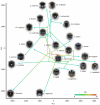
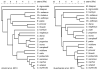
Animal visual signals have the potential to act as an isolating barrier to prevent interbreeding of populations through a role in species recognition. Within communities of competing species, species recognition signals are predicted to undergo character displacement, becoming more visually distinctive from each other; however, this pattern has rarely been identified. Using computational face recognition algorithms to model primate face processing, we demonstrate that the face patterns of guenons (tribe: Cercopithecini) have evolved under selection to become more visually distinctive from those of other guenon species with whom they are sympatric. The relationship between the appearances of sympatric species suggests that distinguishing conspecifics from other guenon species has been a major driver of diversification in guenon face appearance. Visual signals that have undergone character displacement may have had an important role in the tribe's radiation, keeping populations that became geographically separated reproductively isolated on secondary contact.
Figures


References
-
- Pfennig DW, Pfennig KS. Evolution’s Wedge: Competition and the Origins of Diversity. University of California Press; 2013.
-
- Coyne J, Orr H. Speciation. Sinauer Associates; 2004.
-
- Ortiz-Barrientos D, Grealy A, Nosil P. The genetics and ecology of reinforcement: implications for the evolution of prezygotic isolation in sympatry and beyond. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009;1168:156–82. - PubMed
-
- Brown WL, Wilson EO. Character displacement. Syst. Zool. 1956;5:49–64.
-
- Richards-Zawacki CL, Cummings ME. Intraspecific reproductive character displacement in a polymorphic poison dart frog, Dendrobates pumilio. Evolution. 2011;65:259–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

