Identification of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 11E, serovariant 11Av and mixed populations by high-resolution magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (HR-MAS NMR) spectroscopy and flow cytometric serotyping assay (FCSA)
- PMID: 24967818
- PMCID: PMC4072641
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100722
Identification of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 11E, serovariant 11Av and mixed populations by high-resolution magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (HR-MAS NMR) spectroscopy and flow cytometric serotyping assay (FCSA)
Abstract
Background: Recent studies have identified Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 11E and serovariant 11Av among isolates previously typed as 11A by classical serotyping methods. Serotype 11E and serovariant 11Av differ from serotype 11A by having totally or partially inactive wcjE, a gene in cps locus coding for an O-acetyl transferase. Serotype 11E is rare among carriage isolates but common among invasive isolates suggesting that it survives better during invasion. Aim of this work was to investigate the epidemiology of serotype 11A in a pneumococcal collection using a new serotyping approach based on High-Resolution Magic Angle Spinning Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (HR-MAS NMR) spectroscopy to distinguish serotypes 11A and 11E.
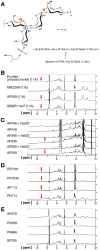
Methods: A collection of 48 (34 invasive and 14 carriage) S. pneumoniae isolates from Italy, previously identified as serotype 11A by the Quellung reaction, were investigated by wcjE sequencing, HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy and the reference flow cytometric serotyping assay (FCSA) based on monoclonal antibodies.
Results: HR-MAS NMR spectra from serotypes 11A and 11E showed different NMR peaks indicating that HR-MAS NMR could be used to distinguish these serotypes, although HR-MAS NMR could not distinguish serotype 11Av from serotype 11E unambiguously. Thirty-eight isolates were confirmed to be serotype 11A, 8 isolates with a mutated wcjE were serotype 11E, 1 isolate belonged to serovariant 11Av, and 1 isolate was a mixed population 11A/11Av. All 11E isolates were identified among invasive isolates.
Conclusions: We proved that HR-MAS NMR can be of potential use for pneumococcal serotyping. The detection of serotype 11E among invasive isolates in our collection, supports previous epidemiological studies suggesting that mutations in wcjE can represent a mechanism promoting pneumococcal survival during invasion. The discovery of a spectrum of immunochemical diversity within established serotypes should stimulate efforts to develop new serotyping approaches.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

