RNA stimulates Aurora B kinase activity during mitosis
- PMID: 24968351
- PMCID: PMC4072698
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100748
RNA stimulates Aurora B kinase activity during mitosis
Abstract
Accurate chromosome segregation is essential for cell viability. The mitotic spindle is crucial for chromosome segregation, but much remains unknown about factors that regulate spindle assembly. Recent work implicates RNA in promoting proper spindle assembly independently of mRNA translation; however, the mechanism by which RNA performs this function is currently unknown. Here, we show that RNA regulates both the localization and catalytic activity of the mitotic kinase, Aurora-B (AurB), which is present in a ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex with many mRNAs. Interestingly, AurB kinase activity is reduced in Xenopus egg extracts treated with RNase, and its activity is stimulated in vitro by RNA binding. Spindle assembly defects following RNase-treatment are partially rescued by inhibiting MCAK, a microtubule depolymerase that is inactivated by AurB-dependent phosphorylation. These findings implicate AurB as an important RNA-dependent spindle assembly factor, and demonstrate a translation-independent role for RNA in stimulating AurB.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

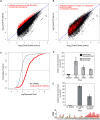

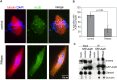


References
-
- Mitchison T, Kirschner M (1984) Microtubule assembly nucleated by isolated centrosomes. Nature 312: 232–237. - PubMed
-
- Heald R, Tournebize R, Blank T, Sandaltzopoulos R, Becker P, et al. (1996) Self-organization of microtubules into bipolar spindles around artificial chromosomes in Xenopus egg extracts. Nature 382: 420–425. - PubMed
-
- Gadde S, Heald R (2004) Mechanisms and molecules of the mitotic spindle. Curr Biol 14: R797–805. - PubMed
-
- Nachury MV, Maresca TJ, Salmon WC, Waterman-Storer CM, Heald R, et al. (2001) Importin beta is a mitotic target of the small GTPase Ran in spindle assembly. Cell 104: 95–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

