Structure and mechanism of an intramembrane liponucleotide synthetase central for phospholipid biosynthesis
- PMID: 24968740
- PMCID: PMC4083444
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms5244
Structure and mechanism of an intramembrane liponucleotide synthetase central for phospholipid biosynthesis
Abstract
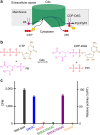
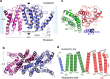
Phospholipids are elemental building-block molecules for biological membranes. Biosynthesis of phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylglycerol and phosphatidylserine requires a central liponucleotide intermediate named cytidine-diphosphate diacylglycerol (CDP-DAG). The CDP-DAG synthetase (Cds) is an integral membrane enzyme catalysing the formation of CDP-DAG, an essential step for phosphoinositide recycling during signal transduction. Here we report the structure of the Cds from Thermotoga maritima (TmCdsA) at 3.4 Å resolution. TmCdsA forms a homodimer and each monomer contains nine transmembrane helices arranged into a novel fold with three domains. An unusual funnel-shaped cavity penetrates half way into the membrane, allowing the enzyme to simultaneously accept hydrophilic substrate (cytidine 5'-triphosphate (CTP)/deoxy-CTP) from cytoplasm and hydrophobic substrate (phosphatidic acid) from membrane. Located at the bottom of the cavity, a Mg(2+)-K(+) hetero-di-metal centre coordinated by an Asp-Asp dyad serves as the cofactor of TmCdsA. The results suggest a two-metal-ion catalytic mechanism for the Cds-mediated synthesis of CDP-DAG at the membrane-cytoplasm interface.
Figures



References
-
- Dowhan W., Bogdanov M. & Mileykovskaya E. inBiochemistry of Lipids, Lipoproteins and Membranes 5th Edn eds Vance D. E., Vance J. E. 1–37Elsevier (2008).
-
- Daum G. inLipid Metabolism and Membrane Biogenesis ed. Daum G. 1–3Springer (2004).
-
- Schneiter R. & Toulmay A. The role of lipids in the biogenesis of integral membrane proteins. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 73, 1224–1232 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

