An effective 5-fluorouracil, levofolinate, and oxaliplatin therapy for recurrent breast cancer: a case report
- PMID: 24969166
- PMCID: PMC4086702
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-8-234
An effective 5-fluorouracil, levofolinate, and oxaliplatin therapy for recurrent breast cancer: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Therapy comprising 5-fluorouracil, levofolinate, and oxaliplatin is currently the most common chemotherapy for colorectal cancer. We experienced a successful case of advanced colon cancer and recurrent breast cancer with 5-fluorouracil, levofolinate, and oxaliplatin therapy.
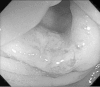
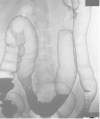
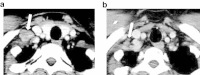
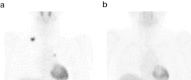
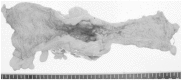
Case presentation: A 43-year-old Japanese woman who had already undergone surgery three times for bilateral breast cancer was admitted to our hospital for the treatment of advanced transverse colon cancer. Preoperative computed tomography demonstrated a swollen lymph node at her right upper clavicle, and fine-needle aspiration biopsy of the lymph node showed that it was a metastasis from the breast cancer. A laparoscopic-assisted colectomy was performed and the pathology demonstrated that the final stage was IIIC (T4aN2aM0, Union for International Cancer Control, 7th edition). The pathological findings and immunohistochemistry showed that the transverse colon tumor was not a metastatic lesion from the breast cancer, but was a de novo colon cancer. Chemotherapy was necessary for both the recurrent breast cancer and the Stage IIIC colon cancer. Therapy of 5-fluorouracil, levofolinate, and oxaliplatin was administered; the therapy included 5-fluorouracil, which is considered to be effective for both colon and breast cancer. After two courses of 5-fluorouracil, levofolinate, and oxaliplatin, the lymph node began to shrink and almost completely disappeared after eight courses of 5-fluorouracil, levofolinate, and oxaliplatin.
Conclusion: We surmise that 5-fluorouracil, levofolinate, and oxaliplatin have the potential to provide a good response for tumors that are sensitive to fluorinated pyrimidine and platinum-containing anticancer drugs such as breast cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Guidelines for Colorectal Cancer. http://www.jsccr.jp/index.html.
-
- Union for International Cancer Control. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. 7. UICC–Wiley-Blackwell; 2009.
-
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. National Institutes of Health. National Cancer Institute. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) National Institutes of Health. National Cancer Institute; 2009. (Version 4.0. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services).
-
- Eisenhauera EA, Therasseb P, Bogaertsc J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther M, Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D, Verweij J. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1) Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:228–247. - PubMed
-
- Saito M. Chemotherapy for breast cancer. Juntendo Med J. 2006;52:546–558.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

