RPL24: a potential therapeutic target whose depletion or acetylation inhibits polysome assembly and cancer cell growth
- PMID: 24970821
- PMCID: PMC4148130
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2099
RPL24: a potential therapeutic target whose depletion or acetylation inhibits polysome assembly and cancer cell growth
Abstract
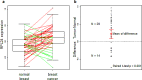
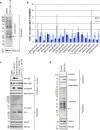
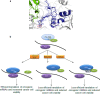
Partial loss of large ribosomal subunit protein 24 (RPL24) function is known to protect mice against Akt or Myc-driven cancers, in part via translational inhibition of a subset of cap(eIF4E)-dependently translated mRNAs. The role of RPL24 in human malignancies is unknown. By analyzing a public dataset of matched human breast cancers and normal mammary tissue, we found that breast cancers express significantly more RPL24 than matched normal breast samples. Depletion of RPL24 in breast cancer cells by >70% reduced cell viability by 80% and decreased protein expression of the eIF4E-dependently translated proteins cyclin D1 (75%), survivin (46%) and NBS1 (30%) without altering GAPDH or beta-tubulin levels. RPL24 knockdown also reduced 80S subunit levels relative to 40S and 60S levels. These effects on expression of eIF4E-dependent proteins and ribosome assembly were mimicked by 2-24 h treatment with the pan-HDACi, trichostatin A (TSA), which induced acetylation of 15 different polysome-associated proteins including RPL24. Furthermore, HDAC6-selective inhibition or HDAC6 knockdown induced ribosomal protein acetylation. Via mass spectrometry, we found that 60S-associated, but not, polysome-associated, RPL24 undergoes HDACi-induced acetylation on K27. Thus, RPL24 K27 acetylation may play a role in ribosome assembly. These findings point toward a novel acetylation-dependent polysome assembly mechanism regulating tumorigenesis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
HDAC6-mediated deacetylation of FLOT2 maintains stability and tumorigenic function of FLOT2 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 May 28;49(5):687-697. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.240077. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 39174882 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
CG0006, a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, induces breast cancer cell death via histone-acetylation and chaperone-disrupting pathways independent of ER status.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Nov;130(2):365-75. doi: 10.1007/s10549-010-1310-4. Epub 2010 Dec 24. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011. PMID: 21184271
-
Effects of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor (HDACi); Trichostatin-A (TSA) on the expression of housekeeping genes.Mol Cell Probes. 2006 Apr;20(2):81-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2005.09.008. Epub 2005 Dec 2. Mol Cell Probes. 2006. PMID: 16326072
-
Troglitazone inhibits histone deacetylase activity in breast cancer cells.Cancer Lett. 2010 Feb 28;288(2):236-50. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2009.07.011. Epub 2009 Aug 20. Cancer Lett. 2010. PMID: 19699029
-
Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid-induced specific epigenetic regulation controls Leptin-induced proliferation of breast cancer cell lines.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):3364-3379. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13764. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27926517 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
In Vivo Investigation of the Effect of Dietary Acrylamide and Evaluation of Its Clinical Relevance in Colon Cancer.Toxics. 2023 Oct 13;11(10):856. doi: 10.3390/toxics11100856. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 37888706 Free PMC article.
-
How Ribosomes Translate Cancer.Cancer Discov. 2017 Oct;7(10):1069-1087. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0550. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Cancer Discov. 2017. PMID: 28923911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ribosome specialization in cancer: a spotlight on ribosomal proteins.NAR Cancer. 2024 Jul 9;6(3):zcae029. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcae029. eCollection 2024 Sep. NAR Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38989007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive analysis of somatic copy number alterations in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Mol Carcinog. 2020 Apr;59(4):412-424. doi: 10.1002/mc.23164. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Mol Carcinog. 2020. PMID: 32039517 Free PMC article.
-
Battle against cancer: an everlasting saga of p53.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Dec 1;15(12):22109-27. doi: 10.3390/ijms151222109. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25470027 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mayer C, Grummt I. Ribosome biogenesis and cell growth: mTOR coordinates transcription by all three classes of nuclear RNA polymerases. Oncogene. 2006;25(48):6384–6391. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

