Mid-adulthood risk factor profiles for CKD
- PMID: 24970884
- PMCID: PMC4214518
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2013070750
Mid-adulthood risk factor profiles for CKD
Abstract
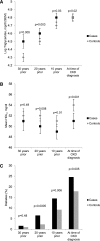
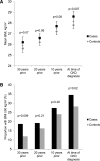
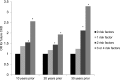
Early identification of CKD risk factors may allow risk factor modification and prevention of CKD progression. We investigated the hypothesis that risk factors are present ≥30 years before the diagnosis of CKD in a case-control study using data from the Framingham Offspring Study. Patients with incident CKD (eGFR≤60 ml/min per 1.73 m2) at examination cycles 6, 7, and 8 were age- and sex-matched 1:2 to patients without CKD at baseline (examination 5). CKD risk factors were measured at each examination cycle. Logistic regression models, adjusted for age, sex, and time period, were constructed to compare risk factor profiles at each time point between cases and controls. During follow-up, 441 new cases of CKD were identified and matched to 882 controls (mean age 69.2 years, 52.4% women). Those who ultimately developed CKD were more likely to have hypertension (odds ratio [OR], 1.76; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.23 to 2.51), obesity (OR, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.14 to 2.59), and higher triglyceride levels (OR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.12 to 1.83) 30 years before CKD diagnosis, and were more likely to have hypertension (OR, 1.38; 95% CI, 1.07 to 1.79), higher triglyceride levels (OR, 1.35; 95% CI, 1.11 to 1.64), lower HDLc (OR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.81 to 0.97), and diabetes (OR, 2.90; 95% CI, 1.59 to 5.29) 20 years before CKD diagnosis. These findings demonstrate that risk factors for CKD are identifiable ≥30 years before diagnosis and suggest the importance of early risk factor identification in patients at risk for CKD.
Keywords: CKD; clinical epidemiology; obesity; risk factors.
Copyright © 2014 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

References
-
- Levey AS, Atkins R, Coresh J, Cohen EP, Collins AJ, Eckardt KU, Nahas ME, Jaber BL, Jadoul M, Levin A, Powe NR, Rossert J, Wheeler DC, Lameire N, Eknoyan G: Chronic kidney disease as a global public health problem: Approaches and initiatives - a position statement from Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes. Kidney Int 72: 247–259, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, Manzi J, Kusek JW, Eggers P, Van Lente F, Levey AS: Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 298: 2038–2047, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Turin TC, Tonelli M, Manns BJ, Ravani P, Ahmed SB, Hemmelgarn BR: Chronic kidney disease and life expectancy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27: 3182–3186, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Matsushita K, van der Velde M, Astor BC, Woodward M, Levey AS, de Jong PE, Coresh J, Gansevoort RT, Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium : Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in general population cohorts: A collaborative meta-analysis. Lancet 375: 2073–2081, 2010 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

