Effect of pentoxifylline on renal function and urinary albumin excretion in patients with diabetic kidney disease: the PREDIAN trial
- PMID: 24970885
- PMCID: PMC4279740
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2014010012
Effect of pentoxifylline on renal function and urinary albumin excretion in patients with diabetic kidney disease: the PREDIAN trial
Abstract
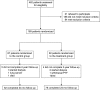
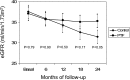
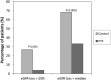
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is the leading cause of ESRD. We conducted an open-label, prospective, randomized trial to determine whether pentoxifylline (PTF), which reduces albuminuria, in addition to renin-angiotensin system (RAS) blockade, can slow progression of renal disease in patients with type 2 diabetes and stages 3-4 CKD. Participants were assigned to receive PTF (1200 mg/d) (n=82) or to a control group (n=87) for 2 years. All patients received similar doses of RAS inhibitors. At study end, eGFR had decreased by a mean±SEM of 2.1±0.4 ml/min per 1.73 m(2) in the PTF group compared with 6.5±0.4 ml/min per 1.73 m(2) in the control group, with a between-group difference of 4.3 ml/min per 1.73 m(2) (95% confidence interval [95% CI], 3.1 to 5.5 ml/min per 1.73 m(2); P<0.001) in favor of PTF. The proportion of patients with a rate of eGFR decline greater than the median rate of decline (0.16 ml/min per 1.73 m(2) per month) was lower in the PTF group than in the control group (33.3% versus 68.2%; P<0.001). Percentage change in urinary albumin excretion was 5.7% (95% CI, -0.3% to 11.1%) in the control group and -14.9% (95% CI, -20.4% to -9.4%) in the PTF group (P=0.001). Urine TNF-α decreased from a median 16 ng/g (interquartile range, 11-20.1 ng/g) to 14.3 ng/g (interquartile range, 9.2-18.4 ng/g) in the PTF group (P<0.01), with no changes in the control group. In this population, addition of PTF to RAS inhibitors resulted in a smaller decrease in eGFR and a greater reduction of residual albuminuria.
Keywords: albuminuria; chronic kidney disease; diabetic nephropathy; inflammation; progression of chronic renal failure.
Copyright © 2015 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures


References
-
- Ritz E, Rychlík I, Locatelli F, Halimi S: End-stage renal failure in type 2 diabetes: A medical catastrophe of worldwide dimensions. Am J Kidney Dis 34: 795–808, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Barnett AH, Bain SC, Bouter P, Karlberg B, Madsbad S, Jervell J, Mustonen J, Diabetics Exposed to Telmisartan and Enalapril Study Group : Angiotensin-receptor blockade versus converting-enzyme inhibition in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 351: 1952–1961, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Eijkelkamp WB, Zhang Z, Remuzzi G, Parving HH, Cooper ME, Keane WF, Shahinfar S, Gleim GW, Weir MR, Brenner BM, de Zeeuw D: Albuminuria is a target for renoprotective therapy independent from blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy: Post hoc analysis from the Reduction of Endpoints in NIDDM with the Angiotensin II Antagonist Losartan (RENAAL) trial. J Am Soc Nephrol 18: 1540–1546, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Packham DK, Wolfe R, Reutens AT, Berl T, Heerspink HL, Rohde R, Ivory S, Lewis J, Raz I, Wiegmann TB, Chan JC, de Zeeuw D, Lewis EJ, Atkins RC, Collaborative Study Group : Sulodexide fails to demonstrate renoprotection in overt type 2 diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 23: 123–130, 2012 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

