Histones and their modifications in ovarian cancer - drivers of disease and therapeutic targets
- PMID: 24971229
- PMCID: PMC4053763
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00144
Histones and their modifications in ovarian cancer - drivers of disease and therapeutic targets
Abstract
Epithelial ovarian cancer has the highest mortality of the gynecological malignancies. High grade serous epithelial ovarian cancer (SEOC) is the most common subtype, with the majority of women presenting with advanced disease where 5-year survival is around 25%. Platinum-based chemotherapy in combination with paclitaxel remains the most effective treatment despite platinum therapies being introduced almost 40 years ago. Advances in molecular medicine are underpinning new strategies for the treatment of cancer. Major advances have been made by international initiatives to sequence cancer genomes. For SEOC, with the exception of TP53 that is mutated in virtually 100% of these tumors, there is no other gene mutated at high frequency. There is extensive copy number variation, as well as changes in methylation patterns that will influence gene expression. To date, the role of histones and their post-translational modifications in ovarian cancer is a relatively understudied field. Post-translational histone modifications play major roles in gene expression as they direct the configuration of chromatin and so access by transcription factors. Histone modifications include methylation, acetylation, and monoubiquitination, with involvement of enzymes including histone methyltransferases, histone acetyltransferases/deacetylases, and ubiquitin ligases/deubiquitinases, respectively. Complexes such as the Polycomb repressive complex also play roles in the control of histone modifications and more recently roles for long non-coding RNA and microRNAs are emerging. Epigenomic-based therapies targeting histone modifications are being developed and offer new approaches for the treatment of ovarian cancer. Here, we discuss histone modifications and their aberrant regulation in malignancy and specifically in ovarian cancer. We review current and upcoming histone-based therapies that have the potential to inform and improve treatment strategies for women with ovarian cancer.
Keywords: deubiquitinases; histone; histone deacetylase inhibitors; histone methyltransferases; lncRNA; ovarian cancer; polycomb repressive complex; splicing.
Figures
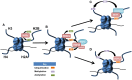
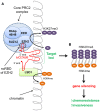
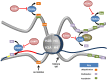
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

