Application of PCR-ELISA in molecular diagnosis
- PMID: 24971343
- PMCID: PMC4058250
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/653014
Application of PCR-ELISA in molecular diagnosis
Abstract
Polymerase chain reaction-enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (PCR-ELISA) is an immunodetection method that can quantify PCR product directly after immobilization of biotinylated DNA on a microplate. This method, which detects nucleic acid instead of protein, is a much more sensitive method compared to conventional PCR method, with shorter analytical time and lower detection limit. Its high specificity and sensitivity, together with its semiquantitative ability, give it a huge potential to serve as a powerful detection tool in various industries such as medical, veterinary, and agricultural industries. With the recent advances in PCR-ELISA, it is envisaged that the assay is more widely recognized for its fast and sensitive detection limit which could improve overall diagnostic time and quality.
Figures
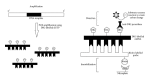
References
-
- Coutlée F, Bobo L, Mayur K, Yolken RH, Viscidi RP. Immunodetection of DNA with biotinylated RNA probes: a study of reactivity of a monoclonal antibody to DNA-RNA hybrids. Analytical Biochemistry. 1989;181(1):96–105. - PubMed
-
- di Pinto A, Terio V, di Pinto P, Colao V, Tantillo G. Detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in shellfish using polymerase chain reaction-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Letters in Applied Microbiology. 2012;54(6):494–498. - PubMed
-
- Pislak M, Ocepek M, Zabavnik-Piano J, Pogacnik M. ProceedIngs of the 7th International Colloquium on Paratuberculosis. Bilbao, Spain: 2003. PCR-ELISA as the method for improving the diagnosis of paratuberculosis; pp. 251–254.
-
- Gill P, Forouzandeh M, Eshraghi N, Ghalami M, Safa M, Noori-Daloii MR. Detection of four β-thalassemia point mutations in Iranians using a PCR-ELISA genotyping system. Molecular and Cellular Probes. 2008;22(2):103–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

