Analysis of metabolites in plasma reveals distinct metabolic features between Dahl salt-sensitive rats and consomic SS.13(BN) rats
- PMID: 24971531
- PMCID: PMC4423742
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.06.089
Analysis of metabolites in plasma reveals distinct metabolic features between Dahl salt-sensitive rats and consomic SS.13(BN) rats
Abstract
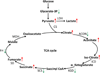
Salt-sensitive hypertension is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disorders. Our previous proteomic study revealed substantial differences in several proteins between Dahl salt-sensitive (SS) rats and salt-insensitive consomic SS.13(BN) rats. Subsequent experiments indicated a role of fumarase insufficiency in the development of hypertension in SS rats. In the present study, a global metabolic profiling study was performed using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) in plasma of SS rats (n=9) and SS.13(BN) rats (n=8) on 0.4% NaCl diet, designed to gain further insights into the relationship between alterations in cellular intermediary metabolism and predisposition to hypertension. Principal component analysis of the data sets revealed a clear clustering and separation of metabolic profiles between SS rats and SS.13(BN) rats. 23 differential metabolites were identified (P<0.05). Higher levels of five TCA cycle metabolites, fumarate, cis-aconitate, isocitrate, citrate and succinate, were observed in SS rats. Pyruvate, which connects TCA cycle and glycolysis, was also increased in SS rats. Moreover, lower activity levels of fumarase, aconitase, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and succinyl-CoA synthetase were detected in the heart, liver or skeletal muscles of SS rats. The distinct metabolic features in SS and SS.13(BN) rats indicate abnormalities of TCA cycle in SS rats, which may play a role in predisposing SS rats to developing salt-sensitive hypertension.
Keywords: Dahl salt-sensitive rats; Hypertension; Mass spectrometry; Metabolomics; TCA cycle.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Novel role of fumarate metabolism in dahl-salt sensitive hypertension.Hypertension. 2009 Aug;54(2):255-60. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.129528. Epub 2009 Jun 22. Hypertension. 2009. PMID: 19546378 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular networks in Dahl salt-sensitive hypertension based on transcriptome analysis of a panel of consomic rats.Physiol Genomics. 2008 Jun 12;34(1):54-64. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00031.2008. Epub 2008 Apr 22. Physiol Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18430809
-
Brown Norway chromosome 13 confers protection from high salt to consomic Dahl S rat.Hypertension. 2001 Feb;37(2 Pt 2):456-61. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.37.2.456. Hypertension. 2001. PMID: 11230318
-
Role of the CYP4A/20-HETE pathway in vascular dysfunction of the Dahl salt-sensitive rat.Clin Sci (Lond). 2013 Jun;124(12):695-700. doi: 10.1042/CS20120483. Clin Sci (Lond). 2013. PMID: 23438293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The renal metabolic mechanism of salt sensitive hypertension in Dahl-SS rats].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2022 Feb 25;74(1):47-58. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35199125 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
β-Aminoisobutyric acid supplementation attenuated salt-sensitive hypertension in Dahl salt-sensitive rats through prevention of insufficient fumarase.Amino Acids. 2022 Feb;54(2):169-180. doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-03092-7. Epub 2021 Nov 27. Amino Acids. 2022. PMID: 34837556
-
Transcriptomic analysis reveals inflammatory and metabolic pathways that are regulated by renal perfusion pressure in the outer medulla of Dahl-S rats.Physiol Genomics. 2018 Jun 1;50(6):440-447. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00034.2018. Epub 2018 Mar 30. Physiol Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29602296 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenic-cell-killing and immunosuppression-inhibiting nanomedicine.Bioact Mater. 2020 Nov 19;6(6):1513-1527. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.11.016. eCollection 2021 Jun. Bioact Mater. 2020. PMID: 33294730 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolites and Hypertension: Insights into Hypertension as a Metabolic Disorder: 2019 Harriet Dustan Award.Hypertension. 2020 Jun;75(6):1386-1396. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.13896. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Hypertension. 2020. PMID: 32336227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of 6-Month Feeding with a Diet Enriched in EPA + DHA from Fish Meat on the Blood Metabolomic Profile of Dogs with Myxomatous Mitral Valve Disease.Animals (Basel). 2021 Nov 24;11(12):3360. doi: 10.3390/ani11123360. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34944135 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weinberger MH, Miller JZ, Luft FC, Grim CE, Fineberg NS. Definitions and characteristics of sodium sensitivity and blood pressure resistance. Hypertension. 1986;8:II127–II134. - PubMed
-
- Morimoto A, Uzu T, Fujii T, Nishimura M, Kuroda S, Nakamura S, Inenaga T, Kimura G. Sodium sensitivity and cardiovascular events in patients with essential hypertension. Lancet. 1997;350:1734–1737. - PubMed
-
- Miyoshi A, Suzuki H, Fujiwara M, Masai M, Iwasaki T. Impairment of endothelial function in salt-sensitive hypertension in humans. Am. J. Hypertens. 1997;10:1083–1090. - PubMed
-
- Cowley AW. The genetic dissection of essential hypertension. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006;7:829–840. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

