Hemodynamic effects of combined focal cerebral ischemia and amyloid protein toxicity in a rat model: a functional CT study
- PMID: 24971942
- PMCID: PMC4074060
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100575
Hemodynamic effects of combined focal cerebral ischemia and amyloid protein toxicity in a rat model: a functional CT study
Abstract
Background/objective: Clinical evidence indicates that cerebral ischemia (CI) and a pathological factor of Alzheimer's disease, the β-amyloid (Aβ) protein, can increase the rate of cognitive impairment in the ageing population. Using the CT Perfusion (CTP) functional imaging, we sought to investigate the interaction between CI and the Aβ protein on cerebral hemodynamics.
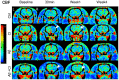
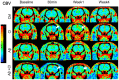
Methods: A previously established rat model of CI and Aβ was used for the CTP study. Iodinated contrast was given intravenously, while serial CT images of sixteen axial slices were acquired. Cerebral blood flow (CBF) and blood volume (CBV) parametric maps were co-registered to a rat brain atlas and regions of interest were drawn on the maps. Microvascular alteration was investigated with histopathology.
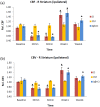
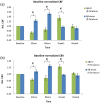
Results: CTP results revealed that ipsilateral striatum of Aβ+CI and CI groups showed significantly lower CBF and CBV than control at the acute phase. Striatal CBF and CBV increased significantly at week 1 in the CI and Aβ+CI groups, but not in the Aβ alone or control group. Histopathology showed that average density of dilated microvessels in the ipsilateral striatum in CI and Aβ+CI groups was significantly higher than control at week 1, indicating this could be associated with hyperperfusion and hypervolemia observed from CTP results.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate that CTP can quantitatively measure the hemodynamic disturbance on CBF and CBV functional maps in a rat model of CI interacting with Aβ.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cerebral blood flow is the optimal CT perfusion parameter for assessing infarct core.Stroke. 2011 Dec;42(12):3435-40. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.618355. Epub 2011 Oct 6. Stroke. 2011. PMID: 21980202
-
C-arm CT measurement of cerebral blood volume and cerebral blood flow using a novel high-speed acquisition and a single intravenous contrast injection.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013 Nov-Dec;34(11):2131-8. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A3536. Epub 2013 May 23. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013. PMID: 23703149 Free PMC article.
-
Flat detector CT in the evaluation of brain parenchyma, intracranial vasculature, and cerebral blood volume: a pilot study in patients with acute symptoms of cerebral ischemia.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010 Sep;31(8):1462-9. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2083. Epub 2010 Apr 8. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010. PMID: 20378700 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Identification of infarct core and penumbra in acute stroke using CT perfusion source images.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010 Jan;31(1):34-9. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1740. Epub 2009 Oct 29. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010. PMID: 19875465 Free PMC article.
-
[Cerebral perfusion CT: theoretical aspects, methodical implementation and clinical experience in the diagnosis of ischemic cerebral infarction].Rofo. 2000 Mar;172(3):210-8. doi: 10.1055/s-2000-109. Rofo. 2000. PMID: 10778450 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Altered Insulin/Insulin-Like Growth Factor Signaling in a Comorbid Rat model of Ischemia and β-Amyloid Toxicity.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 23;8(1):5136. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22985-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29572520 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Delayed Neuroglial Activation in Impaired Cerebral Blood Flow Restoration Following Comorbid Injury.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Apr;40(3):369-380. doi: 10.1007/s10571-019-00735-y. Epub 2019 Sep 14. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 31522299 Free PMC article.
-
The Dynamics of Impaired Blood-Brain Barrier Restoration in a Rat Model of Co-morbid Injury.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Oct;55(10):8071-8083. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-0904-4. Epub 2018 Mar 5. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29508280
-
Effects of cerebral artery thrombectomy on efficacy, safety, cognitive function and peripheral blood Aβ, IL-6 and TNF-α levels in patients with acute cerebral infarction.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Dec 15;13(12):14005-14014. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 35035742 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering of fluorescent or photoactive Trojan probes for detection and eradication of β-Amyloids.Drug Deliv. 2020 Dec;27(1):917-926. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2020.1785048. Drug Deliv. 2020. PMID: 32597244 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seshadri S, Beiser A, Kelly-Hayes M, Kase CS, Au R, et al. (2006) The lifetime risk of stroke. Stroke 37: 345–350. - PubMed
-
- Breteler M (2000) Vascular involvement in cognitive decline and dementia: epidemiologic evidence from the Rotterdam Study and the Rotterdam Scan Study. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 903: 457–465. - PubMed
-
- Song IU, Kim JS, Kim YI, Eah KY, Lee KS (2007) Clinical significance of silent cerebral infarctions in patients with Alzheimer disease. Cognitive and behavioral neurology 20: 93. - PubMed
-
- Vermeer SE, Prins ND, den Heijer T, Hofman A, Koudstaal PJ, et al. (2003) Silent brain infarcts and the risk of dementia and cognitive decline. New England Journal of Medicine 348: 1215–1222. - PubMed
-
- White L (2009) Brain lesions at autopsy in older Japanese-American men as related to cognitive impairment and dementia in the final years of life: a summary report from the Honolulu-Asia aging study. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease 18: 713–725. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

