Synthesis and evaluation of 2,4-disubstituted quinazoline derivatives with potent anti-angiogenesis activities
- PMID: 24972275
- PMCID: PMC6271559
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules19078916
Synthesis and evaluation of 2,4-disubstituted quinazoline derivatives with potent anti-angiogenesis activities
Abstract
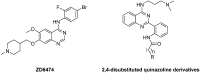
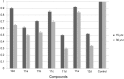
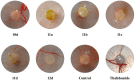
A series of 2,4-disubstituted quinazoline derivatives were designed and synthesized. The biological results showed that most of quinazoline derivatives exhibited potent antiproliferative activities against a panel of three tumor cell lines and a good inhibitory effect against the adhesion and migration of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Among these compounds, 11d was the most potent agent, that also exhibited the highest anti-angiogenesis activities in the chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fong T.A., Shawver L.K., Sun L., Tang C., App H., Powell T.J., Kim Y.H., Schreck R., Wang X., Risau W., et al. SU5416 is a potent and selective inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (Flk-1/KDR) that inhibits tyrosine kinase catalysis, tumor vascularization, and growth of multiple tumor types. Cancer Res. 1999;59:99–106. - PubMed
-
- O’Reilly M.S., Holmgren L., Shing Y., Chen C., Rosenthal R.A., Moses M., Lane W.S., Cao Y., Sage E.H., Folkman J. Angiostatin: A novel angiogenesis inhibitor that mediates the suppression of metastases by a Lewis lung carcinoma. Cell. 1994;79:315–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90200-3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

