Multigenerational exposure to dietary zearalenone (ZEA), an estrogenic mycotoxin, affects puberty and reproduction in female mice
- PMID: 24972337
- PMCID: PMC4137769
- DOI: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2014.06.005
Multigenerational exposure to dietary zearalenone (ZEA), an estrogenic mycotoxin, affects puberty and reproduction in female mice
Abstract
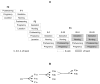
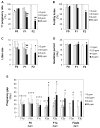
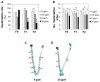
This study investigated potential cumulative effects of multiple pregnancy and multigenerational exposure to dietary ZEA (0, 0.8, 4, or 20ppm) on female puberty and reproduction in C57BL/6J mice. Multiple pregnancies did not significantly affect litter size or offspring puberty. Significant effects were observed in 20ppm ZEA-treated females: advanced puberty onset in F0, F1, and F2 generations; decreased implantation rate, pregnancy rate, and litter size, and increased pregnancy gap and gestation period in F1 and F2 generations; and reduced fertility index in F2 generation. F3 females from 0 and 20ppm groups were split into 0 or 20ppm ZEA diets at weaning, with advanced puberty onset seen in 0-20 and 20-20 groups and decreased implantation rate observed in 20-20 group. In summary, 20ppm dietary ZEA advanced puberty onset without obvious cumulative effect and impaired fertility with multigenerational cumulative effect, which could be partially alleviated upon exposure cessation.
Keywords: Embryo implantation; Female reproduction; Litter size; Multigeneration; Multipregnancy; Vaginal opening; Zearalenone.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
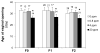
References
-
- Zinedine A, Soriano JM, Molto JC, Manes J. Review on the toxicity, occurrence, metabolism, detoxification, regulations and intake of zearalenone: an oestrogenic mycotoxin. Food Chem Toxicol. 2007;45:1–18. - PubMed
-
- EFSA. Scientific Opinion on the risks for public health related to the presence of zearalenone in food. EFSA Journal. 2011;9:2197.
-
- Massart F, Saggese G. Oestrogenic mycotoxin exposures and precocious pubertal development. Int J Androl. 2010;33:369–76. - PubMed
-
- Deng F, Tao FB, Liu DY, Xu YY, Hao JH, Sun Y, et al. Effects of growth environments and two environmental endocrine disruptors on children with idiopathic precocious puberty. Eur J Endocrinol. 2012;166:803–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

