Full-length haplotype reconstruction to infer the structure of heterogeneous virus populations
- PMID: 24972832
- PMCID: PMC4132706
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku537
Full-length haplotype reconstruction to infer the structure of heterogeneous virus populations
Abstract
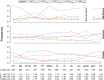
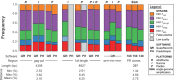
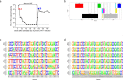
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies enable new insights into the diversity of virus populations within their hosts. Diversity estimation is currently restricted to single-nucleotide variants or to local fragments of no more than a few hundred nucleotides defined by the length of sequence reads. To study complex heterogeneous virus populations comprehensively, novel methods are required that allow for complete reconstruction of the individual viral haplotypes. Here, we show that assembly of whole viral genomes of ∼8600 nucleotides length is feasible from mixtures of heterogeneous HIV-1 strains derived from defined combinations of cloned virus strains and from clinical samples of an HIV-1 superinfected individual. Haplotype reconstruction was achieved using optimized experimental protocols and computational methods for amplification, sequencing and assembly. We comparatively assessed the performance of the three NGS platforms 454 Life Sciences/Roche, Illumina and Pacific Biosciences for this task. Our results prove and delineate the feasibility of NGS-based full-length viral haplotype reconstruction and provide new tools for studying evolution and pathogenesis of viruses.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


References
-
- Nowak M.A. What is a quasispecies? Trends Ecol. Evol. 1992;7:118–121. - PubMed
-
- Metzker M.L. Sequencing technologies—the next generation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010;11:31–46. - PubMed
-
- Macalalad A.R., Zody M.C., Charlebois P., Lennon N.J., Newman R.M., Malboeuf C.M., Ryan E.M., Boutwell C.L., Power K.A., Brackney D.E., et al. Highly sensitive and specific detection of rare variants in mixed viral populations from massively parallel sequence data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012;8:e1002417. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Henn M.R., Boutwell C.L., Charlebois P., Lennon N.J., Power K.A., Macalalad A.R., Berlin A.M., Malboeuf C.M., Ryan E.M., Gnerre S., et al. Whole genome deep sequencing of HIV-1 reveals the impact of early minor variants upon immune recognition during acute infection. PLoS Pathog. 2012;8:e1002529. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

