Common Ewing sarcoma-associated antigens fail to induce natural T cell responses in both patients and healthy individuals
- PMID: 24973179
- PMCID: PMC11028878
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-014-1574-3
Common Ewing sarcoma-associated antigens fail to induce natural T cell responses in both patients and healthy individuals
Abstract
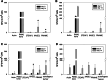
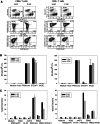
Disseminated or relapsed Ewing sarcoma (EwS) has remained fatal in the majority of patients. A promising approach to preventing relapse after conventional therapy is to establish tumor antigen-specific immune control. Efficient and specific T cell memory against the tumor depends on the expansion of rare T cells with native specificity against target antigens overexpressed by the tumor. Candidate antigens in EwS include six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate-1 (STEAP1), and the human cancer/testis antigens X-antigen family member 1 (XAGE1) and preferentially expressed antigen in melanoma (PRAME). Here, we screened normal donors and EwS patients for the presence of circulating T cells reactive with overlapping peptide libraries of these antigens by IFN-γ Elispot analysis. The majority of 22 healthy donors lacked detectable memory T cell responses against STEAP1, XAGE1 and PRAME. Moreover, ex vivo detection of T cells specific for these antigens in both blood and bone marrow were limited to a minority of EwS patients and required nonspecific T cell prestimulation. Cytotoxic T cells specific for the tumor-associated antigens were efficiently and reliably generated by in vitro priming using professional antigen-presenting cells and optimized cytokine stimulation; however, these T cells failed to interact with native antigen processed by target cells and with EwS cells expressing the antigen. We conclude that EwS-associated antigens fail to induce efficient T cell receptor (TCR)-mediated antitumor immune responses even under optimized conditions. Strategies based on TCR engineering could provide a more effective means to manipulating T cell immunity toward targeted elimination of tumor cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Muller-Berghaus J, Ehlert K, Ugurel S, Umansky V, Bucur M, Schirrmacher V, Beckhove P, Schadendorf D. Melanoma-reactive T cells in the bone marrow of melanoma patients: association with disease stage and disease duration. Cancer Res. 2006;66:5997–6001. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0484. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

