Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-α isoforms and redox state by carotid body neural activity in rats
- PMID: 24973414
- PMCID: PMC4192707
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.273789
Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-α isoforms and redox state by carotid body neural activity in rats
Abstract
Previous studies reported that chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH) results in an imbalanced expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-α (HIF-α) isoforms and oxidative stress in rodents, which may be due either to the direct effect of CIH or indirectly via hitherto uncharacterized mechanism(s). As neural activity is a potent regulator of gene transcription, we hypothesized that carotid body (CB) neural activity contributes to CIH-induced HIF-α isoform expression and oxidative stress in the chemoreflex pathway. Experiments were performed on adult rats exposed to CIH for 10 days. Rats exposed to CIH exhibited: increased HIF-1α and decreased HIF-2α expression; increased NADPH oxidase 2 and decreased superoxide dismutase 2 expression; and oxidative stress in the nucleus tractus solitarius and rostral ventrolateral medulla as well as in the adrenal medulla (AM), a major end organ of the sympathetic nervous system. Selective ablation of the CB abolished these effects. In the AM, sympathetic activation by the CB chemoreflex mediates CIH-induced HIF-α isoform imbalance via muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated Ca(2+) influx, and the resultant activation of mammalian target of rapamycin pathway and calpain proteases. Rats exposed to CIH presented with hypertension, elevated sympathetic activity and increased circulating catecholamines. Selective ablation of either the CB (afferent pathway) or sympathetic innervation to the AM (efferent pathway) abolished these effects. These observations uncover CB neural activity-dependent regulation of HIF-α isoforms and the redox state by CIH in the central and peripheral nervous systems associated with the chemoreflex.
© 2014 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2014 The Physiological Society.
Figures



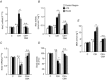


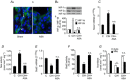
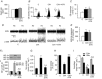

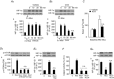
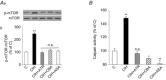

 = 40 ± 3 mmHg, 5 min)-evoked NA and A secretion from adrenal medulla slices is presented as the percentage of basal release. B and C, plasma CA levels of NA and A (B) and MBP (C) are shown. D and E, effect of AIH (15 s at 12% O2, followed by 5 min at 21% O2) on ABP. Representative changes in ABP during pre-AIH, first and 10th AIH, and post-AIH periods (D) and MBP (E) are shown. Data in bar graphs are presented as means ±
= 40 ± 3 mmHg, 5 min)-evoked NA and A secretion from adrenal medulla slices is presented as the percentage of basal release. B and C, plasma CA levels of NA and A (B) and MBP (C) are shown. D and E, effect of AIH (15 s at 12% O2, followed by 5 min at 21% O2) on ABP. Representative changes in ABP during pre-AIH, first and 10th AIH, and post-AIH periods (D) and MBP (E) are shown. Data in bar graphs are presented as means ± References
-
- Caulfield MP, Birdsall NJ. International Union of Pharmacology. XVII. Classification of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1998;50:279–290. - PubMed
-
- Costa-Silva JH, Zoccal DB, Machado BH. Chronic intermittent hypoxia alters glutamatergic control of sympathetic and respiratory activities in the commissural NTS of rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2012;302:R785–R793. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

