Dendritic cells and anergic type I NKT cells play a crucial role in sulfatide-mediated immune regulation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 24973441
- PMCID: PMC4110642
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302898
Dendritic cells and anergic type I NKT cells play a crucial role in sulfatide-mediated immune regulation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
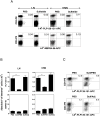
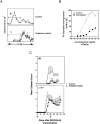
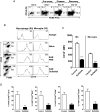
CD1d-restricted NKT cells can be divided into two groups: type I NKT cells use a semi-invariant TCR, whereas type II express a relatively diverse set of TCRs. A major subset of type II NKT cells recognizes myelin-derived sulfatides and is selectively enriched in the CNS tissue during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). We have shown that activation of sulfatide-reactive type II NKT cells by sulfatide prevents induction of EAE. In this article, we have addressed the mechanism of regulation, as well as whether a single immunodominant form of synthetic sulfatide can treat ongoing chronic and relapsing EAE in SJL/J mice. We have shown that the activation of sulfatide-reactive type II NKT cells leads to a significant reduction in the frequency and effector function of myelin proteolipid proteins 139-151/I-A(s)-tetramer(+) cells in lymphoid and CNS tissues. In addition, type I NKT cells and dendritic cells (DCs) in the periphery, as well as CNS-resident microglia, are inactivated after sulfatide administration, and mice deficient in type I NKT cells are not protected from disease. Moreover, tolerized DCs from sulfatide-treated animals can adoptively transfer protection into naive mice. Treatment of SJL/J mice with a synthetic cis-tetracosenoyl sulfatide, but not α-galactosylceramide, reverses ongoing chronic and relapsing EAE. Our data highlight a novel immune-regulatory pathway involving NKT subset interactions leading to inactivation of type I NKT cells, DCs, and microglial cells in suppression of autoimmunity. Because CD1 molecules are nonpolymorphic, the sulfatide-mediated immune-regulatory pathway can be targeted for development of non-HLA-dependent therapeutic approaches to T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases.
Copyright © 2014 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Bendelac A, Savage PB, Teyton L. The biology of NKT cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:297–336. - PubMed
-
- Brigl M, Brenner MB. CD1: antigen presentation and T cell function. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:817–890. - PubMed
-
- Kronenberg M, Rudensky A. Regulation of immunity by self-reactive T cells. Nature. 2005;435:598–604. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

