CXCL17 is a major chemotactic factor for lung macrophages
- PMID: 24973458
- PMCID: PMC4142799
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400551
CXCL17 is a major chemotactic factor for lung macrophages
Abstract
Chemokines are a superfamily of chemotactic cytokines that direct the movement of cells throughout the body under homeostatic and inflammatory conditions. The mucosal chemokine CXCL17 was the last ligand of this superfamily to be characterized. Several recent studies have provided greater insight into the basic biology of this chemokine and have implicated CXCL17 in several human diseases. We sought to better characterize CXCL17's activity in vivo. To this end, we analyzed its chemoattractant properties in vivo and characterized a Cxcl17 (-/-) mouse. This mouse has a significantly reduced number of macrophages in its lungs compared with wild-type mice. In addition, we observed a concurrent increase in a new population of macrophage-like cells that are F4/80(+)CDllc(mid). These results indicate that CXCL17 is a novel macrophage chemoattractant that operates in mucosal tissues. Given the importance of macrophages in inflammation, these observations strongly suggest that CXCL17 is a major regulator of mucosal inflammatory responses.
Copyright © 2014 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures

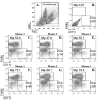

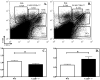

References
-
- Bachelerie F, Ben-Baruch A, Burkhardt AM, Combadiere C, Farber JM, Graham GJ, Horuk R, Sparre-Ulrich AH, Locati M, Luster AD, Mantovani A, Matsushima K, Murphy PM, Nibbs R, Nomiyama H, Power CA, Proudfoot AE, Rosenkilde MM, Rot A, Sozzani S, Thelen M, Yoshie O, Zlotnik A. International Union of Pharmacology. LXXXIX. Update on the extended family of chemokine receptors and introducing a new nomenclature for atypical chemokine receptors. Pharmacological reviews. 2014;66:1–79. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pisabarro MT, Leung B, Kwong M, Corpuz R, Frantz GD, Chiang N, Vandlen R, Diehl LJ, Skelton N, Kim HS, Eaton D, Schmidt KN. Cutting edge: novel human dendritic cell- and monocyte-attracting chemokine-like protein identified by fold recognition methods. J Immunol. 2006;176:2069–2073. - PubMed
-
- Weinstein EJ, Head R, Griggs DW, Sun D, Evans RJ, Swearingen ML, Westlin MM, Mazzarella R. VCC-1, a novel chemokine, promotes tumor growth. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2006;350:74–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

