Redox-sensitive gene-regulatory events controlling aberrant matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression
- PMID: 24973648
- PMCID: PMC4146650
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.06.017
Redox-sensitive gene-regulatory events controlling aberrant matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression
Abstract
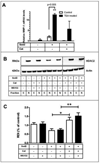
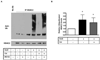
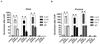
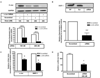
Aberrant matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) expression contributes to the pathogenesis of many degenerative disease processes that are associated with increased oxidative damage or stress. We and others have established that shifts in steady-state H2O2 production resulting from enforced antioxidant gene expression, senescence, or UV irradiation control MMP-1 expression. Here we establish that histone deacetylase-2 (HDAC2) protein levels and its occupancy of the MMP-1 promoter are decreased in response to enforced manganese superoxide dismutase (Sod2) expression. Inhibition of HDAC activity further accentuates the redox-dependent expression of MMP-1. Sod2-dependent decreases in HDAC2 are associated with increases in a proteasome-sensitive pool of ubiquitinylated HDAC2 and MMP-1-specific histone H3 acetylation. Sod2 overexpression also enhanced recruitment of Ets-1, c-Jun, c-Fos, and the histone acetyltransferase PCAF to the distal and proximal regions of the MMP-1 promoter. Furthermore, the Sod2-dependent expression of MMP-1 can be reversed by silencing the transcriptional activator c-Jun. All of the above Sod2-dependent alterations are largely reversed by catalase coexpression, indicating that the redox control of MMP-1 is H2O2-dependent. These findings identify a novel redox regulation of MMP-1 transcription that involves site-specific promoter recruitment of both activating factors and chromatin-modifying enzymes, which converge to maximally drive MMP-1 gene expression.
Keywords: Acetylation; Epigenetic modification; Free radicals; Histone deacetylase-2; Hydrogen peroxide; Manganese superoxide dismutase; Matrix metalloproteinase-1; Oxidative stress; Redox-dependent; Steady-state H(2)O(2) concentration.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Nagase H, Woessner JF., Jr Matrix metalloproteinases. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1999;274:21491–21494. - PubMed
-
- Okada Y, Nagase H, Harris ED., Jr Matrix metalloproteinases 1, 2, and 3 from rheumatoid synovial cells are sufficient to destroy joints. The Journal of rheumatology. 1987;14 Spec No:41–42. - PubMed
-
- Nikkari ST, O'Brien KD, Ferguson M, Hatsukami T, Welgus HG, Alpers CE, Clowes AW. Interstitial collagenase (MMP-1) expression in human carotid atherosclerosis. Circulation. 1995;92:1393–1398. - PubMed
-
- Murray GI, Duncan ME, O'Neil P, Melvin WT, Fothergill JE. Matrix metalloproteinase-1 is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Nature medicine. 1996;2:461–462. - PubMed
-
- Murray GI, Duncan ME, O'Neil P, McKay JA, Melvin WT, Fothergill JE. Matrix metalloproteinase-1 is associated with poor prognosis in oesophageal cancer. The Journal of pathology. 1998;185:256–261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

