Bioengineering paradigms for cell migration in confined microenvironments
- PMID: 24973724
- PMCID: PMC4354884
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2014.06.001
Bioengineering paradigms for cell migration in confined microenvironments
Abstract
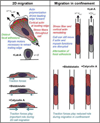
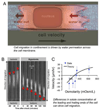
Cell migration is a fundamental process underlying diverse (patho)physiological phenomena. The classical understanding of the molecular mechanisms of cell migration has been based on in vitro studies on two-dimensional substrates. More recently, mounting evidence from intravital studies has shown that during metastasis, tumor cells must navigate complex microenvironments in vivo, including narrow, pre-existing microtracks created by anatomical structures. It is becoming apparent that unraveling the mechanisms of confined cell migration in this context requires a multi-disciplinary approach through integration of in vivo and in vitro studies, along with sophisticated bioengineering techniques and mathematical modeling. Here, we highlight such an approach that has led to discovery of a new model for cell migration in confined microenvironments (i.e., the Osmotic Engine Model).
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Water permeation drives tumor cell migration in confined microenvironments.Cell. 2014 Apr 24;157(3):611-23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.02.052. Epub 2014 Apr 10. Cell. 2014. PMID: 24726433 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor cell migration in complex microenvironments.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Apr;70(8):1335-56. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1115-1. Epub 2012 Aug 25. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 22926411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer cell motility: lessons from migration in confined spaces.Nat Rev Cancer. 2017 Feb;17(2):131-140. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.123. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017. PMID: 27909339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Constructing stem cell microenvironments using bioengineering approaches.Physiol Genomics. 2013 Dec 1;45(23):1123-35. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00099.2013. Epub 2013 Sep 24. Physiol Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24064536 Review.
-
Physical effects of 3-D microenvironments on confined cell behaviors.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Nov 1;327(5):C1192-C1201. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00288.2024. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39246142 Review.
Cited by
-
Interplay of the physical microenvironment, contact guidance, and intracellular signaling in cell decision making.FASEB J. 2016 Jun;30(6):2161-70. doi: 10.1096/fj.201500199R. Epub 2016 Feb 22. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 26902610 Free PMC article.
-
An electro-osmotic microfluidic system to characterize cancer cell migration under confinement.J R Soc Interface. 2019 Jun 28;16(155):20190062. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2019.0062. Epub 2019 Jun 5. J R Soc Interface. 2019. PMID: 31164075 Free PMC article.
-
The interplay between physical cues and mechanosensitive ion channels in cancer metastasis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 7;10:954099. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.954099. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36158191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Mechanics of Single Cell and Collective Migration of Tumor Cells.J Biomech Eng. 2017 Feb 1;139(2):0210051-9. doi: 10.1115/1.4035121. J Biomech Eng. 2017. PMID: 27814431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear Deformation in Response to Mechanical Confinement is Cell Type Dependent.Cells. 2019 May 8;8(5):427. doi: 10.3390/cells8050427. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31072066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reymond N, d'Agua BB, Ridley AJ. Crossing the endothelial barrier during metastasis. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2013;13:858–870. - PubMed
-
- Friedl P, Alexander S. Cancer Invasion the Microenvironment: Plasticity and Reciprocity. Cell. 2011;147:992–1009. - PubMed
-
- Alexander S, Koehl GE, Hirschberg M, Geissler EK, Friedl P. Dynamic imaging of cancer growth and invasion: a modified skin-fold chamber model. Histochemistry and cell biology. 2008;130:1147–1154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

