Fishing for causes and cures of motor neuron disorders
- PMID: 24973750
- PMCID: PMC4073270
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.015719
Fishing for causes and cures of motor neuron disorders
Abstract
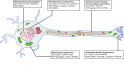
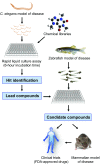
Motor neuron disorders (MNDs) are a clinically heterogeneous group of neurological diseases characterized by progressive degeneration of motor neurons, and share some common pathological pathways. Despite remarkable advances in our understanding of these diseases, no curative treatment for MNDs exists. To better understand the pathogenesis of MNDs and to help develop new treatments, the establishment of animal models that can be studied efficiently and thoroughly is paramount. The zebrafish (Danio rerio) is increasingly becoming a valuable model for studying human diseases and in screening for potential therapeutics. In this Review, we highlight recent progress in using zebrafish to study the pathology of the most common MNDs: spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP). These studies indicate the power of zebrafish as a model to study the consequences of disease-related genes, because zebrafish homologues of human genes have conserved functions with respect to the aetiology of MNDs. Zebrafish also complement other animal models for the study of pathological mechanisms of MNDs and are particularly advantageous for the screening of compounds with therapeutic potential. We present an overview of their potential usefulness in MND drug discovery, which is just beginning and holds much promise for future therapeutic development.
Keywords: ALS; Drug discovery; HSP; Motor neuron disorders; SMA; Zebrafish.
© 2014. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Zebrafish models of human motor neuron diseases: advantages and limitations.Prog Neurobiol. 2014 Jul;118:36-58. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2014.03.001. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Prog Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24705136 Review.
-
Genetic architecture of motor neuron diseases.J Neurol Sci. 2022 Mar 15;434:120099. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2021.120099. Epub 2021 Dec 22. J Neurol Sci. 2022. PMID: 34965490 Review.
-
Exploring Motor Neuron Diseases Using iPSC Platforms.Stem Cells. 2022 Mar 3;40(1):2-13. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxab006. Stem Cells. 2022. PMID: 35511862 Free PMC article.
-
Histone acetylation as a potential therapeutic target in motor neuron degenerative diseases.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(28):5093-104. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990356. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23448465 Review.
-
Diving deep: zebrafish models in motor neuron degeneration research.Front Neurosci. 2024 Jun 20;18:1424025. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1424025. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38966756 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic Analysis of Zebrafish TDP-43 Transgenic Lines.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Dec 13;11:463. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00463. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30618614 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Live Imaging of Axonal Transport in Developing Zebrafish Axons.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2431:325-350. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1990-2_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35412285
-
Therapeutic opportunities and challenges of induced pluripotent stem cells-derived motor neurons for treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and motor neuron disease.Neural Regen Res. 2017 May;12(5):723-736. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.206635. Neural Regen Res. 2017. PMID: 28616022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Great Catch for Investigating Inborn Errors of Metabolism-Insights Obtained from Zebrafish.Biomolecules. 2020 Sep 22;10(9):1352. doi: 10.3390/biom10091352. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32971894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nearly 30 Years of Animal Models to Study Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Historical Overview and Future Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 12;22(22):12236. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212236. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830115 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Achsel T., Barabino S., Cozzolino M., Carrì M. T. (2013). The intriguing case of motor neuron disease: ALS and SMA come closer. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 41, 1593–1597 - PubMed
-
- Akten B., Kye M. J., Hao T., Wertz M. H., Singh S., Nie D., Huang J., Merianda T. T., Twiss J. L., Beattie C. E., et al. (2011). Interaction of survival of motor neuron (SMN) and HuD proteins with mRNA cpg15 rescues motor neuron axonal deficits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 10337–10342 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andersen P. M., Al-Chalabi A. (2011). Clinical genetics of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: what do we really know? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 7, 603–615 - PubMed
-
- Arai T., Hasegawa M., Akiyama H., Ikeda K., Nonaka T., Mori H., Mann D., Tsuchiya K., Yoshida M., Hashizume Y., et al. (2006). TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 351, 602–611 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

