L wave in echo Doppler
- PMID: 24973854
- PMCID: PMC4121743
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ihj.2014.03.022
L wave in echo Doppler
Abstract
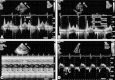
62-year-old female presented with progressive dyspnea NYHA class III for six months. Echocardiography showed normal left ventricular (LV) systolic function, mild biatrial enlargement, an L wave in pulse wave Doppler at mitral inflow and in M mode echocardiography across mitral valve. Tissue Doppler imaging at medial mitral annulus showed an L' wave in mid diastole in addition to E' and A' wave. An L wave in pulse wave Doppler and M mode echocardiography represents continued pulmonary vein mid diastolic flow through the left atrium in to LV across mitral valve after early rapid filling. Presence of an L' wave in these patients associated with higher E/E' is indicative of advance diastolic dysfunction with elevated filling pressures.
Keywords: L wave; Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction; L′ wave; Triphasic mitral inflow.
Copyright © 2014 Cardiological Society of India. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Keren G., Meisner J.S., Sherez J., Yellin E.L., Laniado S. Interrelationship of mid-diastolic mitral valve motion, pulmonary venous flow, and transmitral flow. Circulation. 1986;74:36–44. - PubMed
-
- Ha J.W., Ahn J.A., Moon J.Y. Triphasic mitral inflow velocity with mid-diastolic flow: the presence of mid-diastolic mitral annular velocity indicates advanced diastolic dysfunction. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2006;7:16–21. - PubMed
-
- Ha J.W., Oh J.K., Redfield M.M., Ujino K., Seward J.B., Tajik A.J. Triphasic mitral inflow velocity with middiastolic filling: clinical implications and associated echocardiographic findings. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2004;17:428–431. - PubMed
-
- Lam C.S., Han L., Ha J.W., Oh J.K., Ling L.H. The mitral L wave: a marker of pseudonormal filling and predictor of heart failure in patients with left ventricular hypertrophy. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2005;18:336–341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

