Bluffing promotes overconfidence on social networks
- PMID: 24974793
- PMCID: PMC4074791
- DOI: 10.1038/srep05491
Bluffing promotes overconfidence on social networks
Abstract
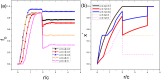
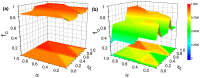
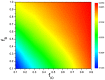
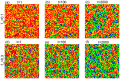
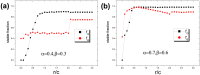
The overconfidence, a well-established bias, in fact leads to unrealistic expectations or faulty assessment. So it remains puzzling why such psychology of self-deception is stabilized in human society. To investigate this problem, we draw lessons from evolutionary game theory which provides a theoretical framework to address the subtleties of cooperation among selfish individuals. Here we propose a spatial resource competition model showing that, counter-intuitively, moderate values rather than large values of resource-to-cost ratio boost overconfidence level most effectively. In contrast to theoretical results in infinite well-mixed populations, network plays a role both as a "catalyst" and a "depressant" in the spreading of overconfidence, especially when resource-to-cost ratio is in a certain range. Moreover, when bluffing is taken into consideration, overconfidence evolves to a higher level to counteract its detrimental effect, which may well explain the prosperity of this "erroneous" psychology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The coevolution of overconfidence and bluffing in the resource competition game.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 17;6:21104. doi: 10.1038/srep21104. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26883799 Free PMC article.
-
The evolution of overconfidence.Nature. 2011 Sep 14;477(7364):317-20. doi: 10.1038/nature10384. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21921915
-
Universal scaling for the dilemma strength in evolutionary games.Phys Life Rev. 2015 Sep;14:1-30. doi: 10.1016/j.plrev.2015.04.033. Epub 2015 May 5. Phys Life Rev. 2015. PMID: 25979121 Review.
-
A potential game approach to modelling evolution in a connected society.Nat Hum Behav. 2019 Jun;3(6):604-610. doi: 10.1038/s41562-019-0571-0. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Nat Hum Behav. 2019. PMID: 30962617
-
Cooperation in a generalized age-structured spatial game.J Theor Biol. 2020 Jan 7;484:109995. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2019.109995. Epub 2019 Sep 3. J Theor Biol. 2020. PMID: 31491496 Review.
Cited by
-
Opinion formation with time-varying bounded confidence.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 6;12(3):e0172982. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172982. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28264038 Free PMC article.
-
The coevolution of overconfidence and bluffing in the resource competition game.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 17;6:21104. doi: 10.1038/srep21104. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26883799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taylor S. & Brown J. Positive illusions and well-being revisited-separating fact from fiction. Psychol. Bull. 116, 21–27 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Eisen C. Confidence: How winning streaks and losing streaks begin and end. Libr. J. 129, 67 (2004).
-
- Dunn D. S. A primer in positive psychology. J. Soc. Clin. Psychol. 27, 896–898 (2008).
-
- Pallier G. The role of individual differences in the accuracy of confidence judgments. J. Gen. Psychol. 129, 257–299 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Koehler J. The psychology of judgment and decision-making. Contemp. Psychol. 40, 315–316 (1995).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

