Clinical outcome of Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly in the rituximab era
- PMID: 24974976
- PMCID: PMC4462402
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12467
Clinical outcome of Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly in the rituximab era
Abstract
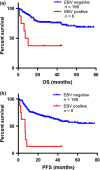
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common subtype of malignant lymphoma. The incidence of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive DLBCL in Asian and Latin American countries ranges from 8 to 10%. The prognosis of patients with EBV-positive DLBCL is controversial. To compare the clinical outcome of EBV-positive and EBV-negative patients with DLBCL in the rituximab era, we analyzed 239 patients with de novo DLBCL diagnosed between January 2007 and December 2011. The presence of EBV in lymphoma cells was detected using EBV-encoded RNA in situ hybridization, and it was found that 18 (6.9%) of 260 patients with diagnosed DLBCL tested positive. Among the 260 cases, 216 cases were treated with rituximab plus chemotherapy, as were 8 EBV-positive DLBCL patients. The median overall survival and progression-free survival times in patients with EBV-positive DLBCL were 8.7 months and 6.8 months, respectively. The median overall survival and progression-free survival could not be determined in EBV-negative DLBCL patients (P = 0.0002, P < 0.0001, respectively). The outcome of patients with EBV-positive DLBCL remains poor, even in the rituximab era.
Keywords: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; Epstein-Barr virus (EBV); prognosis.
© 2014 The Authors. Cancer Science published by Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures

References
-
- Lymphoma Study Group of Japanese Pathologists. The World Health Organization classification of malignant lymphomas in Japan: incidence of recently recognized entities. Pathol Int. 2000;50:696–702. - PubMed
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. 4th edn. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2008.
-
- Gibson SE, Hsi ED. Epstein-Barr virus-positive B-cell lymphoma of the elderly at a United States tertiary medical center: an uncommon aggressive lymphoma with a nongerminal center B-cell phenotype. Hum Pathol. 2009;40:653–61. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

