The α-subunit regulates stability of the metal ion at the ligand-associated metal ion-binding site in β3 integrins
- PMID: 24975416
- PMCID: PMC4132822
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.581470
The α-subunit regulates stability of the metal ion at the ligand-associated metal ion-binding site in β3 integrins
Abstract
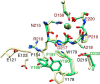
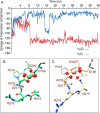
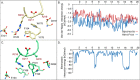
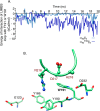
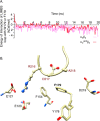
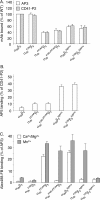
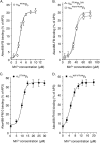
The aspartate in the prototypical integrin-binding motif Arg-Gly-Asp binds the integrin βA domain of the β-subunit through a divalent cation at the metal ion-dependent adhesion site (MIDAS). An auxiliary metal ion at a ligand-associated metal ion-binding site (LIMBS) stabilizes the metal ion at MIDAS. LIMBS contacts distinct residues in the α-subunits of the two β3 integrins αIIbβ3 and αVβ3, but a potential role of this interaction on stability of the metal ion at LIMBS in β3 integrins has not been explored. Equilibrium molecular dynamics simulations of fully hydrated β3 integrin ectodomains revealed strikingly different conformations of LIMBS in unliganded αIIbβ3 versus αVβ3, the result of stronger interactions of LIMBS with αV, which reduce stability of the LIMBS metal ion in αVβ3. Replacing the αIIb-LIMBS interface residue Phe(191) in αIIb (equivalent to Trp(179) in αV) with Trp strengthened this interface and destabilized the metal ion at LIMBS in αIIbβ3; a Trp(179) to Phe mutation in αV produced the opposite but weaker effect. Consistently, an F191/W substitution in cellular αIIbβ3 and a W179/F substitution in αVβ3 reduced and increased, respectively, the apparent affinity of Mn(2+) to the integrin. These findings offer an explanation for the variable occupancy of the metal ion at LIMBS in αVβ3 structures in the absence of ligand and provide new insights into the mechanisms of integrin regulation.
Keywords: Cell Adhesion; Cell Biology; Integrin; Molecular Dynamics; Signal Transduction.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Variation in one residue associated with the metal ion-dependent adhesion site regulates αIIbβ3 integrin ligand binding affinity.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 8;8(10):e76793. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076793. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24116162 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and computational studies of the ligand-associated metal binding site of beta3 integrins.Proteins. 2008 Jun;71(4):1779-91. doi: 10.1002/prot.21859. Proteins. 2008. PMID: 18175315 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane-proximal {alpha}/{beta} stalk interactions differentially regulate integrin activation.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jul 1;280(26):24775-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409548200. Epub 2005 Apr 29. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15863495
-
Beta3 tyrosine phosphorylation in alphaIIbbeta3 (platelet membrane GP IIb-IIIa) outside-in integrin signaling.Thromb Haemost. 2001 Jul;86(1):246-58. Thromb Haemost. 2001. PMID: 11487013 Review.
-
The regulation of integrin function by divalent cations.Cell Adh Migr. 2012 Jan-Feb;6(1):20-9. doi: 10.4161/cam.18702. Cell Adh Migr. 2012. PMID: 22647937 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
β2 Integrins-Multi-Functional Leukocyte Receptors in Health and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 19;21(4):1402. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041402. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32092981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
αIIbβ3: structure and function.J Thromb Haemost. 2015 Jun;13 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S17-25. doi: 10.1111/jth.12915. J Thromb Haemost. 2015. PMID: 26149019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biology and structure of leukocyte β 2 integrins and their role in inflammation.F1000Res. 2016 Oct 4;5:F1000 Faculty Rev-2433. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.9415.1. eCollection 2016. F1000Res. 2016. PMID: 27781085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis of blocking integrin activation and deactivation for anti-inflammation.J Biomed Sci. 2015 Jul 8;22(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12929-015-0159-6. J Biomed Sci. 2015. PMID: 26152212 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hynes R. O. (2002) Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 110, 673–687 - PubMed
-
- Moser M., Legate K. R., Zent R., Fässler R. (2009) The tail of integrins, talin, and kindlins. Science 324, 895–899 - PubMed
-
- Hu D. D., Barbas C. F., Smith J. W. (1996) An allosteric Ca2+ binding site on the β3-integrins that regulates the dissociation rate for RGD ligands. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 21745–21751 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

