A role for Tac2, NkB, and Nk3 receptor in normal and dysregulated fear memory consolidation
- PMID: 24976214
- PMCID: PMC4103970
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.05.028
A role for Tac2, NkB, and Nk3 receptor in normal and dysregulated fear memory consolidation
Abstract
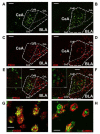
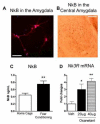
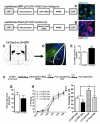
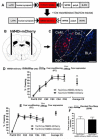
The centromedial amygdala (CeM), a subdivision of the central amygdala (CeA), is believed to be the main output station of the amygdala for fear expression. We provide evidence that the Tac2 gene, expressed by neurons specifically within the CeM, is required for modulating fear memories. Tac2 is colocalized with GAD65 and CaMKIIα but not with PKCd and Enk neurons in the CeM. Moreover, the Tac2 product, NkB, and its specific receptor, Nk3R, are also involved in the consolidation of fear memories. Increased Tac2 expression, through a stress-induced PTSD-like model, or following lentiviral CeA overexpression, are sufficient to enhance fear consolidation. This effect is blocked by the Nk3R antagonist osanetant. Concordantly, silencing of Tac2-expressing neurons in CeA with DREADDs impairs fear consolidation. Together, these studies further our understanding of the role of the Tac2 gene and CeM in fear processing and may provide approaches to intervention for fear-related disorders.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition, Text Revision (DSM5) American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC: 2013.
-
- Almli LM, Mercer KB, Kerley K, Feng H, Bradley B, Conneely KN, Ressler KJ. ADCYAP1R1 genotype associates with post-traumatic stress symptoms in highly traumatized African-American females. American journal of medical genetics Part B, Neuropsychiatric genetics: the official publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics. 2013;162B:262–272. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

