Systems analysis and the prediction and prevention of Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 24976265
- PMCID: PMC5931209
- DOI: 10.1016/j.copbio.2014.05.007
Systems analysis and the prediction and prevention of Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
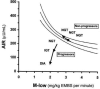
Prevalence of Type 2 diabetes has increased at an alarming rate, highlighting the need to correctly predict the development of this disease in order to allow intervention and thus, slow progression of the disease and resulting metabolic derangement. There have been many recent 'advances' geared toward the detection of pre-diabetes, including genome wide association studies and metabolomics. Although these approaches generate a large amount of data with a single blood sample, studies have indicated limited success using genetic and metabolomics information alone for identification of disease risk. Clinical assessment of the disposition index (DI), based on the hyperbolic law of glucose tolerance, is a powerful predictor of Type 2 diabetes, but is not easily assessed in the clinical setting. Thus, it is evident that combining genetic or metabolomic approaches for a more simple assessment of DI may provide a useful tool to identify those at highest risk for Type 2 diabetes, allowing for intervention and prevention.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Diabetes Surveillance System
-
- The White House, Office of the Press Secretary National Diabetes Month, 2013 [Press release] 2013 Retrieved from http://www.whitehouse.gov/the-press-office/2013/10/31/presidential-procl....
-
- Timmer Jens. [January 2, 2014];Definition of Systems Biology. 2014 from http://www.zbsa.de/Systems-Biology/defn.
-
- Perreault L, Pan Q, Mather KJ, Watson KE, Hamman RF, Kahn SE. Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Effect of regression from prediabetes to normal glucose regulation on long-term reduction in diabetes risk: results from the Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study. Lancet. 2012;379:2243–51. [Restoration of normal glucose regulation significantly reduces incidence of diabetes in individuals at high risk for development of Type 2 diabetes, underlining the importance of correctly identifying those with insulin resistance.] - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

