Novel treatment options for perforations of the upper gastrointestinal tract: endoscopic vacuum therapy and over-the-scope clips
- PMID: 24976714
- PMCID: PMC4069305
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7767
Novel treatment options for perforations of the upper gastrointestinal tract: endoscopic vacuum therapy and over-the-scope clips
Abstract
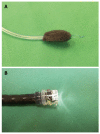
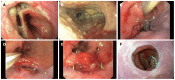
Endoscopic management of leakages and perforations of the upper gastrointestinal tract has gained great importance as it avoids the morbidity and mortality of surgical intervention. In the past years, covered self-expanding metal stents were the mainstay of endoscopic therapy. However, two new techniques are now available that enlarge the possibilities of defect closure: endoscopic vacuum therapy (EVT), and over-the-scope clip (OTSC). EVT is performed by mounting a polyurethane sponge on a gastric tube and placing it into the leakage. Continuous suction is applied via the tube resulting in effective drainage of the cavity and the induction of wound healing, comparable to the application of vacuum therapy in cutaneous wounds. The system is changed every 3-5 d. The overall success rate of EVT in the literature ranges from 84% to 100%, with a mean of 90%; only few complications have been reported. OTSCs are loaded on a transparent cap which is mounted on the tip of a standard endoscope. By bringing the edges of the perforation into the cap, by suction or by dedicated devices, such as anchor or twin grasper, the OTSC can be placed to close the perforation. For acute endoscopy associated perforations, the mean success rate is 90% (range: 70%-100%). For other types of perforations (postoperative, other chronic leaks and fistulas) success rates are somewhat lower (68%, and 59%, respectively). Only few complications have been reported. Although first reports are promising, further studies are needed to define the exact role of EVT and OTSC in treatment algorithms of upper gastrointestinal perforations.
Keywords: Endoscopic vacuum therapy; Endoscopy; Fistula; Over-the-scope clip; Perforation; Upper gastrointestinal.
Figures
References
-
- Junemann-Ramirez M, Awan MY, Khan ZM, Rahamim JS. Anastomotic leakage post-esophagogastrectomy for esophageal carcinoma: retrospective analysis of predictive factors, management and influence on longterm survival in a high volume centre. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2005;27:3–7. - PubMed
-
- Voermans RP, Le Moine O, von Renteln D, Ponchon T, Giovannini M, Bruno M, Weusten B, Seewald S, Costamagna G, Deprez P, et al. Efficacy of endoscopic closure of acute perforations of the gastrointestinal tract. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;10:603–608. - PubMed
-
- Schorsch T, Müller C, Loske G. Endoscopic vacuum therapy of anastomotic leakage and iatrogenic perforation in the esophagus. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:2040–2045. - PubMed
-
- Biancari F, D’Andrea V, Paone R, Di Marco C, Savino G, Koivukangas V, Saarnio J, Lucenteforte E. Current treatment and outcome of esophageal perforations in adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of 75 studies. World J Surg. 2013;37:1051–1059. - PubMed
-
- Clavien PA, Barkun J, de Oliveira ML, Vauthey JN, Dindo D, Schulick RD, de Santibañes E, Pekolj J, Slankamenac K, Bassi C, et al. The Clavien-Dindo classification of surgical complications: five-year experience. Ann Surg. 2009;250:187–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

