Hypericum Perforatum Decreased Hippocampus TNF-α and Corticosterone Levels with No Effect on Kynurenine/Tryptophan Ratio in Bilateral Ovariectomized Rats
- PMID: 24976763
- PMCID: PMC4071176
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.3.233
Hypericum Perforatum Decreased Hippocampus TNF-α and Corticosterone Levels with No Effect on Kynurenine/Tryptophan Ratio in Bilateral Ovariectomized Rats
Abstract
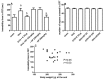
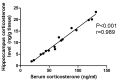
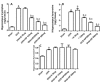
The present study was designed to investigate the effect Hypericum Perforatum (HP), on behavioral changes, corticosterone, TNF-α levels and tryptophan metabolism and disposition in bilateral ovariectomized rats compared to 17α -ethinylestradiol. Behavioral analysis by measuring immobility time in forced swimming test and open field test, serum and hippocampal corticosterone and TNF-α along with hippocampal kynurenine/tryptophan ratio were determined in mature ovariectomized rats treated orally either by HP at three different doses 125, 250, and 500 mg/kg/day or by 17α-ethinylestradiol 30 µg/kg/day for 30 days. Ovariectomized rats showed significant increase in immobility time in the forced swimming test. Along with elevation in serum and hippocampal TNF-α and corticosterone levels associated with significant increase in hippocampal kynurenine/tryptophan ratio. Immobility time in the forced swimming test was decreased in rats treated by different doses of HP in a dose dependent manner and 17α-ethinylestradiol with no concomitant changes in the open field test. Only Rats treated with HP exhibited significant decrease in the elevated serum and hippocampal TNF-α and corticosterone, which couldn't explain the associated insignificant effect on hippocampaus kynurenine/tryptophan ratio in comparison to ovariectomized untreated rats. It is concluded that increased tryptophan metabolism toward kynurenine secondary to elevated corticosterone and TNF-α might be one of the pathohphysiological mechanisms that could explain depression like state observed in this rat model. Further, the observed attenuating effect of HP on TNF-α and corticosterone could contribute in its antidepressant effect in this animal model by other ways than their effects on tryptophan-kynurenine metabolism pathway.
Keywords: Corticosterone; Hypericum perforatum; Kyninurenine; TNF-α; Tryptophan.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interferon-alpha treatment induces depression-like behaviour accompanied by elevated hippocampal quinolinic acid levels in rats.Behav Brain Res. 2015 Oct 15;293:166-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.07.015. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Behav Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 26205824
-
Lipopolysaccharide repeated challenge followed by chronic mild stress protocol introduces a combined model of depression in rats: reversibility by imipramine and pentoxifylline.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2014 Nov;126:152-62. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2014.09.014. Epub 2014 Sep 28. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2014. PMID: 25268312
-
Hypericum perforatum treatment: effect on behaviour and neurogenesis in a chronic stress model in mice.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2011 Jan 27;11:7. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-11-7. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2011. PMID: 21272291 Free PMC article.
-
Naringenin protects against oxido-inflammatory aberrations and altered tryptophan metabolism in olfactory bulbectomized-mice model of depression.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2018 Sep 15;355:257-268. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2018.07.010. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30017640
-
Genetic and hormonal regulation of tryptophan kynurenine metabolism: implications for vascular cognitive impairment, major depressive disorder, and aging.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Dec;1122:35-49. doi: 10.1196/annals.1403.003. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 18077563 Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis with TNFα inhibitors does not affect serum levels of tryptophan metabolites.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Oct;31(5):2393-2400. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01317-7. Epub 2023 Aug 30. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37646896 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Indoleamine 2, 3-Dioxygenase, a Biomarker for Tuberculosis in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Patients.Clin Infect Dis. 2017 Oct 15;65(8):1356-1358. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix550. Clin Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 29017244 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between plasma TNF-α levels and agitation symptoms in first episode patients with schizophrenia.BMC Psychiatry. 2024 Jul 2;24(1):480. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-05796-y. BMC Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38956509 Free PMC article.
-
St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) and depression: what happens to the neurotransmitter systems?Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022 Jun;395(6):629-642. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02229-z. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35294606 Review.
-
Neuroprotective Natural Products' Regulatory Effects on Depression via Gut-Brain Axis Targeting Tryptophan.Nutrients. 2022 Aug 10;14(16):3270. doi: 10.3390/nu14163270. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36014776 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Llaneza P, García-Portilla MP, Llaneza-Suárez D, Armott B, Pérez-López FR. Depressive disorders and the menopause transition. Maturitas. 2012;71:120–130. - PubMed
-
- Maes M, Smith R, Scharpe S. The monocyte-T-lymphocyte hypothesis of major depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1995;20:111–116. - PubMed
-
- Simen BB, Duman CH, Simen AA, Duman RS. TNFalpha signaling in depression and anxiety: behavioral consequences of individual receptor targeting. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;59:775–785. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

