Lamotrigine decreased hippocampal damage and improved vascular risk markers in a rat model of pentylenetetrazole induced kindling seizure
- PMID: 24976768
- PMCID: PMC4071181
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.3.269
Lamotrigine decreased hippocampal damage and improved vascular risk markers in a rat model of pentylenetetrazole induced kindling seizure
Abstract
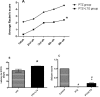
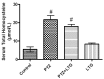
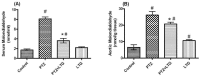
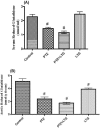
Various antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) especially enzyme-inducing AEDs might be associated with increased vascular risk, through impairment of the endogenous antioxidative ability which may trigger oxygen-dependent tissue injury. Lamotrigine (LTG) a non-enzyme-inducing AED has scarce information regarding its effects on oxidative stress. The present study aimed to study the possible modulation of vascular risk factors of epileptogenesis by LTG, in a rat model of kindling seizure induced by pentylenetetrazole (PTZ). Four groups of male Wister rats were used; vehicle control group, PTZ group (alternate day PTZ, 30 mg/kg, i.p), LTG/PTZ group (LTG 20 mg/kg/day p.o and alternate day PTZ) and LTG group. The study period was 5 weeks. Lipoproteins and total homocysteine (tHcy), malondialdehyde (MDA) and reduced glutathione (GSH) were measured. Aortic endothelial function study and histopathological examination of the rats' brains, aortas and coronaries were conducted. Serum total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), tHcy, MDA, GSH levels were significantly higher in epileptic rats than normal controls rats. A decrease in HDL-cholesterol with high atherosclerotic index was also demonstrated. The administration of LTG improved the PTZ-kindled seizures. It produced a significant decrease in TC, TG and LDL-cholesterol, MDA, aortic GSH and increase in HDL-cholesterol with no significant effect on serum GSH and tHcy levels. LTG improved endothelium-dependent relaxation, decreased hippocampal neurodegenerative changes and atherosclerotic changes of aortas and coronaries. LTG decreased seizures severity, hippocampal damage and improved vascular risk markers in this rat model of kindling seizures.
Keywords: Antiepileptic drugs; Epilepsy; Homocysteine; Lamotrigine; Pentylenetetrazole.
Figures
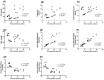
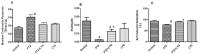
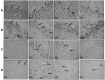

 ) and smooth muscle cells (▲). Notice tunica adventitia is thin. (2) PTZ treated rat: clumps of cells with darkly stained nuclei (↑) attached to the endothelium of tunica intima which is apparently irregular. Few of the smooth muscle cells of tunica media show foamy acidophilic cytoplasm with karyolitic nucleus (▲) or clearly vacuolated cytoplasm with peripheral flat pyknotic nucleus (↑↑). (3) PTZ-LTG treated rat: apparently regular tunica intima (↑). Most of the smooth muscle cells are nearly similar to control group, others show foamy acidophilic cytoplasm (↑↑) and few number shows vacuolated cytoplasm with deeply stained nucleus (▲). (4) LTG treated rat: tunicae of the aorta are nearly similar to the control group. Row B, A photomicrograph of a section a coronary artery of the heart (H&E, ×540); (1) Control rat: an intact endothelial lining (↑). The tunica media (M) is formed of smooth muscle fibres with rod shaped vesicular nuclei (▲). The adventitia (A) is formed of loose connective tissue. (2) PTZ treated rat: multiple vacuoles in the tunica intima and tunica media (↑). Notice adherence of blood elements to the endothelium (▲). Exudates are also seen (
) and smooth muscle cells (▲). Notice tunica adventitia is thin. (2) PTZ treated rat: clumps of cells with darkly stained nuclei (↑) attached to the endothelium of tunica intima which is apparently irregular. Few of the smooth muscle cells of tunica media show foamy acidophilic cytoplasm with karyolitic nucleus (▲) or clearly vacuolated cytoplasm with peripheral flat pyknotic nucleus (↑↑). (3) PTZ-LTG treated rat: apparently regular tunica intima (↑). Most of the smooth muscle cells are nearly similar to control group, others show foamy acidophilic cytoplasm (↑↑) and few number shows vacuolated cytoplasm with deeply stained nucleus (▲). (4) LTG treated rat: tunicae of the aorta are nearly similar to the control group. Row B, A photomicrograph of a section a coronary artery of the heart (H&E, ×540); (1) Control rat: an intact endothelial lining (↑). The tunica media (M) is formed of smooth muscle fibres with rod shaped vesicular nuclei (▲). The adventitia (A) is formed of loose connective tissue. (2) PTZ treated rat: multiple vacuoles in the tunica intima and tunica media (↑). Notice adherence of blood elements to the endothelium (▲). Exudates are also seen ( ). (3) PTZ-LTG treated rat: few vacuolated cells are seen in tunica media (↑). (4) LTG treated rat: nearly intact tunicae.
). (3) PTZ-LTG treated rat: few vacuolated cells are seen in tunica media (↑). (4) LTG treated rat: nearly intact tunicae.Similar articles
-
Effect of lamotrigine on epilepsy-induced cognitive impairment and hippocampal neuronal apoptosis in pentylenetetrazole-kindled animal model.Synapse. 2017 Feb;71(2). doi: 10.1002/syn.21945. Epub 2016 Dec 1. Synapse. 2017. PMID: 27733018
-
Protective effects of lamotrigine and vitamin B12 on pentylenetetrazole-induced epileptogenesis in rats.Epilepsy Behav. 2021 May;118:107915. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2021.107915. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Epilepsy Behav. 2021. PMID: 33743341
-
Omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids enhance the protective effect of levetiracetam against seizures, cognitive impairment and hippocampal oxidative DNA damage in young kindled rats.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015 Aug;135:105-13. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2015.05.020. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015. PMID: 26044965
-
Evaluation of antiepileptic effect of S-adenosyl methionine and its role in memory impairment in pentylenetetrazole-induced kindling model in rats.Epilepsy Behav. 2016 Aug;61:153-157. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2016.05.024. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Epilepsy Behav. 2016. PMID: 27344504
-
Comparison and effects of acute lamotrigine treatment on extracellular excitatory amino acids in the hippocampus of PTZ-kindled epileptic and PTZ-induced status epilepticus rats.Neurochem Res. 2013 Mar;38(3):504-11. doi: 10.1007/s11064-012-0942-7. Epub 2012 Dec 11. Neurochem Res. 2013. PMID: 23229790
Cited by
-
Utilizing Andrographis paniculata leaves and roots by effective usage of the bioactive andrographolide and its nanodelivery: investigation of antikindling and antioxidant activities through in silico and in vivo studies.Front Nutr. 2023 May 31;10:1185236. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1185236. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37324729 Free PMC article.
-
Second Generation of Antiepileptic Drugs and Oxidative Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 15;24(4):3873. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043873. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Oxidative Stress in Epilepsy-Focus on Melatonin.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 2;25(23):12943. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312943. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
One-carbon cycle alterations induced by Dyrk1a dosage.Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2014 Nov 21;1:487-492. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2014.11.004. eCollection 2014. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2014. PMID: 27896129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nikolaos T, Stylianos G, Chryssoula N, Irini P, Christos M, Dimitrios T, Konstantinos P, Antonis T. The effect of long-term antiepileptic treatment on serum cholesterol (TC, HDL, LDL) and triglyceride levels in adult epileptic patients on monotherapy. Med Sci Monit. 2004;10:MT50–MT52. - PubMed
-
- Attilakos A, Papakonstantinou E, Schulpis K, Voudris K, Katsarou E, Mastroyianni S, Garoufi A. Early effect of sodium valproate and carbamazepine monotherapy on homocysteine metabolism in children with epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2006;71:229–232. - PubMed
-
- Sudha K, Rao AV, Rao A. Oxidative stress and antioxidants in epilepsy. Clin Chim Acta. 2001;303:19–24. - PubMed
-
- Tan TY, Lu CH, Chuang HY, Lin TK, Liou CW, Chang WN, Chuang YC. Long-term antiepileptic drug therapy contributes to the acceleration of atherosclerosis. Epilepsia. 2009;50:1579–1586. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

