Efficient conversion of solar energy to biomass and electricity
- PMID: 24976951
- PMCID: PMC4062565
- DOI: 10.1186/2046-9063-10-4
Efficient conversion of solar energy to biomass and electricity
Abstract
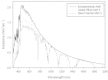
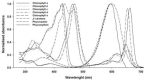
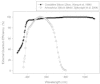
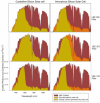
The Earth receives around 1000 W.m(-2) of power from the Sun and only a fraction of this light energy is able to be converted to biomass (chemical energy) via the process of photosynthesis. Out of all photosynthetic organisms, microalgae, due to their fast growth rates and their ability to grow on non-arable land using saline water, have been identified as potential source of raw material for chemical energy production. Electrical energy can also be produced from this same solar resource via the use of photovoltaic modules. In this work we propose a novel method of combining both of these energy production processes to make full utilisation of the solar spectrum and increase the productivity of light-limited microalgae systems. These two methods of energy production would appear to compete for use of the same energy resource (sunlight) to produce either chemical or electrical energy. However, some groups of microalgae (i.e. Chlorophyta) only require the blue and red portions of the spectrum whereas photovoltaic devices can absorb strongly over the full range of visible light. This suggests that a combination of the two energy production systems would allow for a full utilization of the solar spectrum allowing both the production of chemical and electrical energy from the one facility making efficient use of available land and solar energy. In this work we propose to introduce a filter above the algae culture to modify the spectrum of light received by the algae and redirect parts of the spectrum to generate electricity. The electrical energy generated by this approach can then be directed to running ancillary systems or producing extra illumination for the growth of microalgae. We have modelled an approach whereby the productivity of light-limited microalgae systems can be improved by at least 4% through using an LED array to increase the total amount of illumination on the microalgae culture.
Keywords: Biofuel; Microalgae; Photovoltaics; Renewable; Solar energy.
Figures

References
-
- Neckel H, Labs D. The solar radiation between 3300 and 12500 Å. Sol Phys. 1984;90:205–258.
-
- ASTM. Book Standard Tables for Reference Solar Spectral Irradiances: Direct Normal and Hemispherical on 37° Tilted Surface, Volume G 173–03. City: ASTM; 2008. Standard Tables for Reference Solar Spectral Irradiances: direct Normal and Hemispherical on 37° Tilted Surface.
-
- Gueymard CA, Myers D, Emery K. Proposed reference irradiance spectra for solar energy systems testing. Sol Energy. 2002;73:443–467. doi: 10.1016/S0038-092X(03)00005-7. - DOI
-
- Borowitzka MA. eLS. Volume. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2012. Phycology. doi:10.1002/9780470015902.a0000334.pub3.
-
- Moheimani NR, Borowitzka MA. Limits to productivity of the alga Pleurochrysis carterae (Haptophyta) grown in outdoor raceway ponds. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2006;96:27–36. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

