The epidemiology and demographics of slipped capital femoral epiphysis
- PMID: 24977061
- PMCID: PMC4063129
- DOI: 10.5402/2011/486512
The epidemiology and demographics of slipped capital femoral epiphysis
Abstract
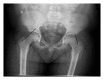
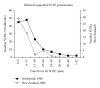
The etiology of slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE) is unknown with many insights coming from epidemiologic/demographic information. A systematic medical literature review regarding SCFE was performed. The incidence is 0.33/100,000 to 24.58/100,000 children 8 to 15 years of age. The relative racial frequency, relative to Caucasians at 1.0, is 5.6 for Polynesians, 3.9 for Blacks, and 2.5 for Hispanics. The average age is 12.0 years for boys and 11.2 years for girls. The physiologic age when SCFE occurs is less variable than the chronologic age. The average symptom duration is 4 to 5 months. Most children are obese: >50% are >95th percentile weight for age with average BMI is 25-30 kg/m(2). The onset of SCFE is in the summer when north of 40°N. Bilaterality ranges from 18 to 50%. In children with bilateral involvement, 50-60% present with simultaneous SCFEs and those who present with a unilateral SCFE and subsequently develop a contralateral SCFE do so within 18 months. The age at presentation is younger for those who present with a unilateral SCFE and later develop a contralateral SCFE. The age-weight, age-height, and height test are useful to differentiate between an idiopathic and atypical SCFE.
Figures







References
-
- Schein AJ. Acute severe slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 1967;51:151–166. - PubMed
-
- Segal LS, Weitzel PP, Davidson RS. Valgus slipped capital femoral epiphysis: fact or fiction? Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 1996;(322):91–98. - PubMed
-
- Loder RT, O’Donnell PW, Didelot WP, Kayes KJ. Valgus slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics. 2006;26(5):594–600. - PubMed
-
- Yngve DA, Moulton DL, Evans EB. Valgus slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics B. 2005;14(3):172–176. - PubMed
-
- Loder RT, Wittenberg B, DeSilva G. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis associated with endocrine disorders. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics. 1995;15(3):349–356. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
