The absolute bioavailability of racemic ketamine from a novel sublingual formulation
- PMID: 24977293
- PMCID: PMC4093926
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.12264
The absolute bioavailability of racemic ketamine from a novel sublingual formulation
Abstract
Aim: The principal study objective was to investigate the pharmacokinetic characteristics of a new sublingual ketamine wafer and to establish its absolute bioavailability and local tolerability.
Methods: The study was of open label, two way randomized crossover design in eight healthy male volunteers. Each participant received either a single 10 mg intravenous dose as a constant rate 30 min infusion or a 25mg sublingual dose of ketamine wafer in two treatment periods with a 7 day wash out. Pharmacokinetic blood sampling and local tolerability and safety assessments were carried out during 24 h following both dosing occasions. Plasma concentrations were analyzed by non-compartmental methods and local tolerability was assessed using modified Likert scales.
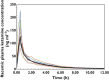
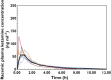
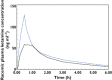
Results: The median (90% CI lower, upper limit) absolute bioavailability of sublingual ketamine was 29% (27, 31%). The first quantifiable plasma ketamine concentration was observed within 5 min for all eight participants for both routes of administration and the median (min–max) time of the peak plasma concentration was 0.75 h (0.25–1.0 h) after sublingual administration. The ketamine wafer had very good local tolerability.
Conclusion: Sublingual administration of the ketamine wafer resulted in rapid absorption. The ketamine wafer has comparable bioavailability with other oral transmucosal formulations of ketamine but with markedly reduced inter-subject variability, warranting further evaluation as an analgesic adjunct.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

