GPU-accelerated non-uniform fast Fourier transform-based compressive sensing spectral domain optical coherence tomography
- PMID: 24977582
- PMCID: PMC4083058
- DOI: 10.1364/OE.22.014871
GPU-accelerated non-uniform fast Fourier transform-based compressive sensing spectral domain optical coherence tomography
Abstract
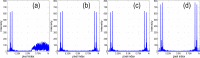
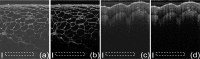
We implemented the graphics processing unit (GPU) accelerated compressive sensing (CS) non-uniform in k-space spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD OCT). Kaiser-Bessel (KB) function and Gaussian function are used independently as the convolution kernel in the gridding-based non-uniform fast Fourier transform (NUFFT) algorithm with different oversampling ratios and kernel widths. Our implementation is compared with the GPU-accelerated modified non-uniform discrete Fourier transform (MNUDFT) matrix-based CS SD OCT and the GPU-accelerated fast Fourier transform (FFT)-based CS SD OCT. It was found that our implementation has comparable performance to the GPU-accelerated MNUDFT-based CS SD OCT in terms of image quality while providing more than 5 times speed enhancement. When compared to the GPU-accelerated FFT based-CS SD OCT, it shows smaller background noise and less side lobes while eliminating the need for the cumbersome k-space grid filling and the k-linear calibration procedure. Finally, we demonstrated that by using a conventional desktop computer architecture having three GPUs, real-time B-mode imaging can be obtained in excess of 30 fps for the GPU-accelerated NUFFT based CS SD OCT with frame size 2048(axial) × 1,000(lateral).
Figures

References
-
- Donoho D. L., “Compressed sensing,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52(4), 1289–1306 (2006). 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 - DOI
-
- Candes E. J., Romberg J., Tao T., “Robust uncertainty principles: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information,” Inf. Theory 52(2), 489–509 (2006). 10.1109/TIT.2005.862083 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

