Receptor for advanced glycation end-products regulates lung fluid balance via protein kinase C-gp91(phox) signaling to epithelial sodium channels
- PMID: 24978055
- PMCID: PMC5455303
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2014-0002OC
Receptor for advanced glycation end-products regulates lung fluid balance via protein kinase C-gp91(phox) signaling to epithelial sodium channels
Abstract
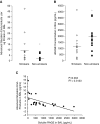
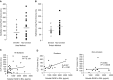
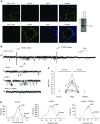
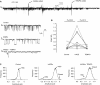
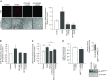
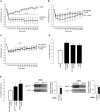
The receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE), a multiligand member of the Ig family, may play a crucial role in the regulation of lung fluid balance. We quantified soluble RAGE (sRAGE), a decoy isoform, and advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) from the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of smokers and nonsmokers, and tested the hypothesis that AGEs regulate lung fluid balance through protein kinase C (PKC)-gp91(phox) signaling to the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC). Human bronchoalveolar lavage samples from smokers showed increased AGEs (9.02 ± 3.03 μg versus 2.48 ± 0.53 μg), lower sRAGE (1,205 ± 292 pg/ml versus 1,910 ± 263 pg/ml), and lower volume(s) of epithelial lining fluid (97 ± 14 ml versus 133 ± 17 ml). sRAGE levels did not predict ELF volumes in nonsmokers; however, in smokers, higher volumes of ELF were predicted with higher levels of sRAGE. Single-channel patch clamp analysis of rat alveolar epithelial type 1 cells showed that AGEs increased ENaC activity measured as the product of the number of channels (N) and the open probability (Po) (NPo) from 0.19 ± 0.08 to 0.83 ± 0.22 (P = 0.017) and the subsequent addition of 4-hydroxy-2, 2, 6, 6-tetramethylpiperidine-N-oxyl decreased ENaC NPo to 0.15 ± 0.07 (P = 0.01). In type 2 cells, human AGEs increased ENaC NPo from 0.12 ± 0.05 to 0.53 ± 0.16 (P = 0.025) and the addition of 4-hydroxy-2, 2, 6, 6-tetramethylpiperidine-N-oxyl decreased ENaC NPo to 0.10 ± 0.03 (P = 0.013). Using molecular and biochemical techniques, we observed that inhibition of RAGE and PKC activity attenuated AGE-induced activation of ENaC. AGEs induced phosphorylation of p47(phox) and increased gp91(phox)-dependent reactive oxygen species production, a response that was abrogated with RAGE or PKC inhibition. Finally, tracheal instillation of AGEs promoted clearance of lung fluid, whereas concomitant inhibition of RAGE, PKC, and gp91(phox) abrogated the response.
Keywords: acute respiratory distress syndrome; alveolar microenvironment; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; lung injury; pulmonary edema.
Figures

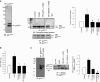
References
-
- Schmidt AM, Yan SD, Yan SF, Stern DM. The biology of the receptor for advanced glycation end products and its ligands. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1498:99–111. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt AM, Stern DM. Receptor for AGE (RAGE) is a gene within the major histocompatibility class III region: implications for host response mechanisms in homeostasis and chronic disease. Front Biosci. 2001;6:D1151–D1160. - PubMed
-
- Crapo JD, Barry BE, Gehr P, Bachofen M, Weibel ER. Cell number and cell characteristics of the normal human lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982;126:332–337. - PubMed
-
- Fehrenbach H, Kasper M, Tschernig T, Shearman MS, Schuh D, Muller M. Receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (RAGE) exhibits highly differential cellular and subcellular localisation in rat and human lung. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy -le-grand) 1998;44:1147–1157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

