The "Sniffin' Kids" test--a 14-item odor identification test for children
- PMID: 24979650
- PMCID: PMC4076236
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101086
The "Sniffin' Kids" test--a 14-item odor identification test for children
Abstract
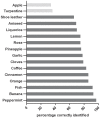
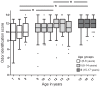
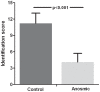
Tools for measuring olfactory function in adults have been well established. Although studies have shown that olfactory impairment in children may occur as a consequence of a number of diseases or head trauma, until today no consensus on how to evaluate the sense of smell in children exists in Europe. Aim of the study was to develop a modified "Sniffin' Sticks" odor identification test, the "Sniffin' Kids" test for the use in children. In this study 537 children between 6-17 years of age were included. Fourteen odors, which were identified at a high rate by children, were selected from the "Sniffin' Sticks" 16-item odor identification test. Normative date for the 14-item "Sniffin' Kids" odor identification test was obtained. The test was validated by including a group of congenital anosmic children. Results show that the "Sniffin' Kids" test is able to discriminate between normosmia and anosmia with a cutoff value of >7 points on the odor identification test. In addition the test-retest reliability was investigated in a group of 31 healthy children and shown to be ρ = 0.44. With the 14-item odor identification "Sniffin' Kids" test we present a valid and reliable test for measuring olfactory function in children between ages 6-17 years.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The "Sniffin' Kids-PT" test: A smell test variant for Portuguese children.Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2024 Mar;141(2):69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.anorl.2023.12.003. Epub 2024 Jan 17. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2024. PMID: 38238186
-
Extended version of the "Sniffin' Sticks" identification test: test-retest reliability and validity.J Neurosci Methods. 2015 Mar 30;243:111-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.01.034. Epub 2015 Feb 10. J Neurosci Methods. 2015. PMID: 25677404
-
[Clinical application of Sniffin' Sticks olfactory psychophysical measurements].Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013 Sep;48(9):741-5. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24330876 Chinese.
-
Assessment of Olfactory Function in Children and Adolescents: An Overview.Chem Senses. 2021 Jan 1;46:bjab027. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjab027. Chem Senses. 2021. PMID: 34237138 Review.
-
[Clinical aspects of dysosmia and presentation of European Olfactory Test of "sniffin sticks": a review].J Otolaryngol. 2005 Apr;34(2):86-92. doi: 10.2310/7070.2005.00086. J Otolaryngol. 2005. PMID: 16076406 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Development of the Spanish Version of Sniffin's Sticks Olfactory Identification Test: Normative Data and Validity of Parallel Measures.Brain Sci. 2021 Feb 10;11(2):216. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11020216. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 33578970 Free PMC article.
-
Updated Sniffin' Sticks normative data based on an extended sample of 9139 subjects.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Mar;276(3):719-728. doi: 10.1007/s00405-018-5248-1. Epub 2018 Dec 15. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 30554358 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory threshold and odor discrimination ability in children - evaluation of a modified "Sniffin' Sticks" test.Sci Rep. 2017 May 16;7(1):1928. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01465-1. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28512302 Free PMC article.
-
Elexacaftor-Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor Improves Sinonasal Outcomes in Young Children With Cystic Fibrosis.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2025 Jul;15(7):706-714. doi: 10.1002/alr.23555. Epub 2025 Mar 2. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2025. PMID: 40024881 Free PMC article.
-
Subtle olfactory dysfunction after SARS-CoV-2 virus infection in children.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2021 Jan;140:110539. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2020.110539. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 33307419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gudziol V, Lotsch J, Hahner A, Zahnert T, Hummel T (2006) Clinical significance of results from olfactory testing. Laryngoscope 116: 1858–1863. - PubMed
-
- Doty RL, Shaman P, Dann M (1984) Development of the University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test: a standardized microencapsulated test of olfactory function. Physiol Behav 32: 489–502. - PubMed
-
- Hummel T, Kobal G, Gudziol H, Mackay-Sim A (2007) Normative data for the "Sniffin' Sticks" including tests of odor identification, odor discrimination, and olfactory thresholds: an upgrade based on a group of more than 3,000 subjects. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 264: 237–243. - PubMed
-
- Kobal G, Hummel T, Sekinger B, Barz S, Roscher S, et al. (1996) "Sniffin' sticks": screening of olfactory performance. Rhinology 34: 222–226. - PubMed
-
- Kondo H, Matsuda T, Hashiba M, Baba S (1998) A study of the relationship between the T&T olfactometer and the University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test in a Japanese population. Am J Rhinol 12: 353–358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

